Downregulation of N6-methyladenosine binding YTHDF2 protein mediated by miR-493-3p suppresses prostate cancer by elevating N6-methyladenosine levels
- PMID: 29423080
- PMCID: PMC5790497
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.23365
Downregulation of N6-methyladenosine binding YTHDF2 protein mediated by miR-493-3p suppresses prostate cancer by elevating N6-methyladenosine levels
Abstract
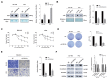
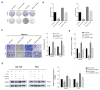
Recent evidence suggests that m6A modifications regulate the progressions of several types of tumors. YTHDF2, an m6A reader, has been implicated in the regulation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). miR-493-3p has been defined as tumor suppressor that inhibits the progressions of several types of cancers. However, the functions and mechanisms of YTHDF2 and the indirect m6A regulated role of miR-493-3p in prostate cancer (PCa) remains to be elusive. In this study, immuno-histochemical (IHC) staining and chromogenic in situ hybridization (CISH) were performed to find YTHDF2 was frequently upregulated but miR-493-3p was downregulated in both PCa tissues and cell lines (DU-145 and PC3) which was negatively correlated with each other. Knock down of YTHDF2 significantly elevated m6A levels, and inhibited the cell proliferation and migration of DU-145 and PC3 cell lines. The dual-luciferase reporter assay confirmed YTHDF2 as the direct target of miR-493-3p. In addition, forced expression of miR-493-3p consistently elevated the m6A levels and inhibited proliferation and migration with the knock down of YTHDF2. In contrast, overexpression of YTHDF2 and inhibition of miR-493-3p conversely reduced m6A levels. Additionally, the rescue experiments revealed that inhibition of miR-493-3p abrogated the suppression of proliferation and migration induced by si-YTHDF2. To conclude, YTHDF2 and miR-493-3p, as two crucial m6A regulators, are involved in the progression of PCa by indirectly modulating m6A levels. In view of these promising results, YTHDF2 and miR-493-3p may provide new insights into the carcinogenesis and new potential therapeutic targets for PCa.
Keywords: PCa; YTHDF2; epigenetics; m6A; miR-493-3p.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Activation of the KDM5A/miRNA-495/YTHDF2/m6A-MOB3B axis facilitates prostate cancer progression.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 21;39(1):223. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01735-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33087165 Free PMC article.
-
YTHDF2, a protein repressed by miR-145, regulates proliferation, apoptosis, and migration in ovarian cancer cells.J Ovarian Res. 2020 Sep 18;13(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s13048-020-00717-5. J Ovarian Res. 2020. PMID: 32948220 Free PMC article.
-
YTHDF2 mediates the mRNA degradation of the tumor suppressors to induce AKT phosphorylation in N6-methyladenosine-dependent way in prostate cancer.Mol Cancer. 2020 Oct 29;19(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01267-6. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33121495 Free PMC article.
-
The biological function of m6A reader YTHDF2 and its role in human disease.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Feb 16;21(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01807-0. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 33593354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
m6A binding protein YTHDF2 in cancer.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2022 Apr 5;11(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s40164-022-00269-y. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35382893 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of writers, erasers and readers within miRNA-related m6A modification in cancers.Cell Prolif. 2023 Jan;56(1):e13340. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13340. Epub 2022 Sep 26. Cell Prolif. 2023. PMID: 36162823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the ALKBH5 RNA demethylase in invasive breast cancer.Discov Oncol. 2024 Aug 11;15(1):343. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01205-8. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39127986 Free PMC article.
-
RNA N6-methyladenosine modifications in urological cancers: from mechanism to application.Nat Rev Urol. 2024 Aug;21(8):460-476. doi: 10.1038/s41585-023-00851-x. Epub 2024 Feb 12. Nat Rev Urol. 2024. PMID: 38347160 Review.
-
The role of the methyltransferase METTL3 in prostate cancer: a potential therapeutic target.BMC Cancer. 2024 Jan 2;24(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11741-1. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38166703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of RNA modification in urological cancers: mechanisms and clinical potential.Discov Oncol. 2023 Dec 20;14(1):235. doi: 10.1007/s12672-023-00843-8. Discov Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38117350 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

