Design of miRNA sponges for MDV-1 as a therapeutic strategy against lymphomas
- PMID: 29423087
- PMCID: PMC5790504
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.23379
Design of miRNA sponges for MDV-1 as a therapeutic strategy against lymphomas
Abstract
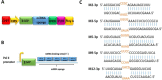
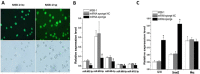
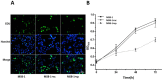
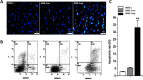
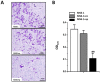
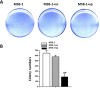
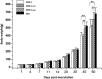
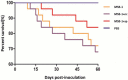
Lymphomas are solid-type tumors containing lymphoid cells. Some of latent herpesvirus infections established in B and/or T-lymphocytes could result in the formation of lymphomas. Marek's disease virus serotype 1 (MDV-1) is an avian herpes virus causing to lymphoproliferative tumors in birds, known as Marek's disease (MD). MD has often been used as an ideal biological model for studying the pathogenesis of lymphoma diseases caused by viruses. Therefore, we used it as a research subject to study the effect of miRNA sponges on its tumorigenicity, and to develop the theoretical basis for a new anti-tumor small molecule. The miRNA sponges designed in this study specifically bind to and degrade the miRNAs of meq gene cluster of MDV-1, including miR-M2-3p, miR-M3-5p, miR-M5-3p, miR-M9-5p and miR-M12-3p.qPCR results showed that the knockdown efficiency was 85.03%, 74.97%, 47.06%, 75.33% and 62.55%, respectively. EDU staining and CCK-8 results showed that miRNA sponges inhibited the proliferation of MDV-1 transformed MSB-1 cells in vitro, and the proliferation rate of miRNA sponges-treated cells was about 50% of the control group. DAPI staining and Annxin V-FITC/PI double staining showed that miRNA sponges induced apoptosis in MSB-1 cells, and the apoptotic rate was increased by about 27.87% compared with the control group. The results of transwell showed that miRNA sponges could inhibit the invasion of MSB-1 cells in vitro, and the inhibitory rate was about 64.52%. The soft agar assay showed that miRNA sponges could inhibit the tumorigenic ability of MSB-1 cells in vitro, and the inhibitory rate was about 66.44%.The 60-days animal study showed that miRNA sponges could alleviate the growth inhibition of MSB-1 cells (about 14.78%) and reduce the mortality (about 16.00%). In addition, the tumor formation rate was 0 (8-12% in the control group).This study suggests that miRNA sponges can serve as an effective anti-tumor small molecule for the tumors caused by herpesvirus, with potential clinical implications.
Keywords: MSB-1 cell; marek’s disease virus 1; meq miRNA cluster; miRNA sponge; tumorigenicity.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
Marek's Disease Virus (Gallid alphaherpesvirus 2)-Encoded miR-M2-5p Simultaneously Promotes Cell Proliferation and Suppresses Apoptosis Through RBM24 and MYOD1-Mediated Signaling Pathways.Front Microbiol. 2020 Nov 3;11:596422. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.596422. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33224130 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs 221 and 222 target p27Kip1 in Marek's disease virus-transformed tumour cell line MSB-1.J Gen Virol. 2009 May;90(Pt 5):1164-1171. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.007831-0. Epub 2009 Mar 4. J Gen Virol. 2009. PMID: 19264608
-
Current state of Marek's disease virus microRNA research.Avian Dis. 2013 Jun;57(2 Suppl):332-9. doi: 10.1637/10355-090812-Review.1. Avian Dis. 2013. PMID: 23901744 Review.
-
Virus-encoded miR-155 ortholog is an important potential regulator but not essential for the development of lymphomas induced by very virulent Marek's disease virus.Virology. 2014 Jan 5;448:55-64. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.09.017. Epub 2013 Oct 20. Virology. 2014. PMID: 24314636
Cited by
-
Viral miRNA delivered by exosomes from Marek's disease virus-transformed lymphoma cell line exerts regulatory function in internalized primary chicken embryo fibroblast cells.Tumour Virus Res. 2024 Dec;18:200286. doi: 10.1016/j.tvr.2024.200286. Epub 2024 Jun 22. Tumour Virus Res. 2024. PMID: 38914377 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-Coordinated Schizophrenia Risk Network Cross-Talk With Cardiovascular Repair and Opposed Gliomagenesis.Front Genet. 2020 Mar 4;11:149. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00149. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32194626 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of v-rel-Induced Oncogenesis through microRNA Targeting.Viruses. 2018 May 5;10(5):242. doi: 10.3390/v10050242. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 29734737 Free PMC article.
-
Critical roles of non-coding RNAs in lifecycle and biology of Marek's disease herpesvirus.Sci China Life Sci. 2023 Feb;66(2):251-268. doi: 10.1007/s11427-022-2258-4. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Sci China Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 36617590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temperature-induced reactivation of Marek's disease virus-transformed T cells ex vivo.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Mar 8;10:1145757. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1145757. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 36968465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkin DM. The global health burden of infection-associated cancers in the year 2002. Int J Cancer. 2006;118:3030–3044. - PubMed
-
- Gates AE, Kaplan LD. AIDS malignancies in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Oncology (Williston Park) 2002;16:441–451. - PubMed
-
- Grulich AE, van Leeuwen MT, Falster MO, Vajdic CM. Incidence of cancers in people with HIV/AIDS compared with immunosuppressed transplant recipients: a meta-analysis. Lancet. 2007;370:59–67. - PubMed
-
- Biggs PM, Nair V. The long view: 40 years of Marek’s disease research and Avian Pathology. Avian Pathol. 2012;41:3–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

