Time trends of the prevalence of allergic diseases in Korea: A systematic literature review
- PMID: 29423375
- PMCID: PMC5796968
- DOI: 10.5415/apallergy.2018.8.e8
Time trends of the prevalence of allergic diseases in Korea: A systematic literature review
Abstract
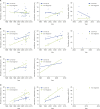
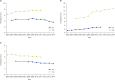
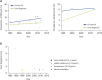
The prevalence of allergic diseases has increased dramatically in recent decades, and are now considered major chronic diseases at the global level. The increasing burden of allergic diseases has led to numerous worldwide and local researchers to investigate the time trends in its prevalence and identify its driving factors. Environmental changes such as urbanization and industrialization have been suggested to explain the increasing prevalence, but recent reports from Western countries suggest that this prevalence has reached a plateau or even possibly, started to decrease. However, such environmental changes are still occurring in many Asia-Pacific countries, including Korea, and it is speculated that the peak in allergy epidemics has yet to come. The present systematic literature review aimed to explore the time trends in the prevalence of allergic diseases in Korea and to identify the unmet needs for facilitating further studies.
Keywords: Allergic diseases; Epidemiology; Incidence; Korea; Prevalence; Trends.
Figures

References
-
- Song WJ, Wong GW. Changing trends and challenges in the management of asthma in Asia. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;140:1272–1274. - PubMed
-
- Nicolaou N, Siddique N, Custovic A. Allergic disease in urban and rural populations: increasing prevalence with increasing urbanization. Allergy. 2005;60:1357–1360. - PubMed
-
- Pawankar R, Canonica GW, Holgate ST, Lockey RF, Blaiss MS. World Allergy Organisation (WAO) white book on allergy: update 2013. Milwaukee (WI): World Allergy Organization; 2013.
-
- Anandan C, Nurmatov U, van Schayck OC, Sheikh A. Is the prevalence of asthma declining? Systematic review of epidemiological studies. Allergy. 2010;65:152–167. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
