Sex differences in binge-like EtOH drinking, corticotropin-releasing hormone and corticosterone: effects of β-endorphin
- PMID: 29424043
- PMCID: PMC6082742
- DOI: 10.1111/adb.12610
Sex differences in binge-like EtOH drinking, corticotropin-releasing hormone and corticosterone: effects of β-endorphin
Abstract
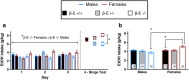
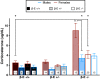
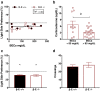
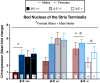
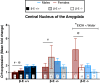
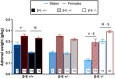
Binge drinking is an increasingly common pattern of risky use associated with numerous health problems, including alcohol use disorders. Because low basal plasma levels of β-endorphin (β-E) and an increased β-E response to alcohol are evident in genetically at-risk human populations, this peptide is thought to contribute to the susceptibility for disordered drinking. Animal models suggest that the effect of β-E on consumption may be sex-dependent. Here, we studied binge-like EtOH consumption in transgenic mice possessing varying levels of β-E: wild-type controls with 100% of the peptide (β-E +/+), heterozygous mice constitutively modified to possess 50% of wild-type levels (β-E +/-) and mice entirely lacking the capacity to synthesize β-E (-/-). These three genotypes and both sexes were evaluated in a 4-day, two-bottle choice, drinking in the dark paradigm with limited access to 20% EtOH. β-E deficiency determined sexually divergent patterns of drinking in that β-E -/- female mice drank more than their wild-type counterparts, an effect not observed in male mice. β-E -/- female mice also displayed elevated basal anxiety, plasma corticosterone and corticotropin-releasing hormone mRNA in the extended amygdala, and all of these were normalized by EtOH self-administration. These data suggest that a heightened risk for excessive EtOH consumption in female mice is related to the drug's ability to ameliorate an overactive anxiety/stress-like state. Taken together, our study highlights a critical impact of sex on neuropeptide regulation of EtOH consumption.
Keywords: BNST; CRF; CeA; HPA axis; POMC; stress.
© 2018 The Authors.Addiction Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society for the Study of Addiction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronic Voluntary Binge Ethanol Consumption Causes Sex-Specific Differences in Microglial Signaling Pathways and Withdrawal-associated Behaviors in Mice.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2020 Sep;44(9):1791-1806. doi: 10.1111/acer.14420. Epub 2020 Sep 6. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2020. PMID: 32767774
-
Sex and β-Endorphin Influence the Effects of Ethanol on Limbic Gabra2 Expression in a Mouse Binge Drinking Model.Front Genet. 2018 Nov 29;9:567. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00567. eCollection 2018. Front Genet. 2018. PMID: 30555510 Free PMC article.
-
Corticotropin Releasing Factor Binding Protein and CRF2 Receptors in the Ventral Tegmental Area: Modulation of Ethanol Binge Drinking in C57BL/6J Mice.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2015 Sep;39(9):1609-18. doi: 10.1111/acer.12825. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2015. PMID: 26247973 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical evidence implicating corticotropin-releasing factor signaling in ethanol consumption and neuroadaptation.Genes Brain Behav. 2015 Jan;14(1):98-135. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12189. Genes Brain Behav. 2015. PMID: 25565358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synaptic effects induced by alcohol.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2013;13:31-86. doi: 10.1007/7854_2011_143. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 21786203 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Modulates Binge-Like Ethanol Drinking in a Sex-Dependent Manner: Impact of Amygdala Deletion and Inhibition of a Central Amygdala to Lateral Hypothalamus Circuit.Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2024 Oct 25;5(1):100405. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsgos.2024.100405. eCollection 2025 Jan. Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2024. PMID: 39660275 Free PMC article.
-
Three Weeks of Binge Alcohol Drinking Generates Increased Alcohol Front-Loading and Robust Compulsive-Like Alcohol Drinking in Male and Female C57BL/6J Mice.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021 Mar;45(3):650-660. doi: 10.1111/acer.14563. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021. PMID: 33496972 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting CRF Projections from the Central Amygdala to Lateral Hypothalamus and Amygdala Deletion of CRF Alters Binge-Like Ethanol Drinking in a Sex-Dependent Manner.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 13:2024.04.09.588750. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.09.588750. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2024 Oct 25;5(1):100405. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsgos.2024.100405. PMID: 38645149 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Activation of the dorsal septum increases alcohol consumption in male C57BL/6J mice.Addict Neurosci. 2022 Sep;3:100023. doi: 10.1016/j.addicn.2022.100023. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Addict Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36034165 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Phosphodiesterase-7A (PDE7A) as a Novel Target for Reducing Ethanol Consumption in Mice.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2024 Aug 1;27(8):pyae032. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyae032. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39099166 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

