LncRNAs in vascular biology and disease
- PMID: 29425892
- PMCID: PMC6078824
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vph.2018.01.003
LncRNAs in vascular biology and disease
Abstract
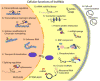
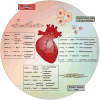
Accumulating studies indicate that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play important roles in the regulation of diverse biological processes involved in homeostatic control of the vessel wall in health and disease. However, our knowledge of the mechanisms by which lncRNAs control gene expression and cell signaling pathways is still nascent. Furthermore, only a handful of lncRNAs has been functionally evaluated in response to pathophysiological stimuli or in vascular disease states. For example, lncRNAs may regulate endothelial dysfunction by modulating endothelial cell proliferation (e.g. MALAT1, H19) or angiogenesis (e.g. MEG3, MANTIS). LncRNAs have also been implicated in modulating vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) phenotypes or vascular remodeling (e.g. ANRIL, SMILR, SENCR, MYOSLID). Finally, emerging studies have implicated lncRNAs in leukocytes activation (e.g. lincRNA-Cox2, linc00305, THRIL), macrophage polarization (e.g. GAS5), and cholesterol metabolism (e.g. LeXis). This review summarizes recent findings on the expression, mechanism, and function of lncRNAs implicated in a range of vascular disease states from mice to human subjects. An improved understanding of lncRNAs in vascular disease may provide new pathophysiological insights and opportunities for the generation of a new class of RNA-based biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; lncRNAs; non-coding RNAs; vascular biology.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Hartge MM, Unger T, Kintscher U. The endothelium and vascular inflammation in diabetes. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2007;4:84–88. - PubMed
-
- Virchow R. Cellular pathology. As based upon physiological and pathological histology. Lecture XVI--Atheromatous affection of arteries. 1858. Nutr Rev. 1989;47:23–25. - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Everett BM, Thuren T, MacFadyen JG, Chang WH, Ballantyne C, Fonseca F, Nicolau J, Koenig W, Anker SD, et al. Antiinflammatory Therapy with Canakinumab for Atherosclerotic Disease. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:1119–1131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

