Surveillance Imaging and Alpha Fetoprotein for Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients With Cirrhosis: A Meta-analysis
- PMID: 29425931
- PMCID: PMC5927818
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.01.064
Surveillance Imaging and Alpha Fetoprotein for Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients With Cirrhosis: A Meta-analysis
Abstract
Background & aims: Society guidelines differ in their recommendations for surveillance to detect early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in patients with cirrhosis. We compared the performance of surveillance imaging, with or without alpha fetoprotein (AFP), for early detection of HCC in patients with cirrhosis.
Methods: Two reviewers searched MEDLINE and SCOPUS from January 1990 through August 2016 to identify published sensitivity and specificity of surveillance strategies for overall and early detection of HCC. Pooled estimates were calculated and compared using the DerSimonian and Laird method for a random effects model. The study was conducted in accordance with Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analysis guidelines.
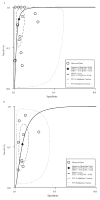
Results: Thirty-two studies (comprising 13,367 patients) characterized sensitivity of imaging with or without AFP measurement for detection of HCC in patients with cirrhosis. Ultrasound detected any stage HCC with 84% sensitivity (95% confidence interval [CI] 76%-92%), but early-stage HCC with only 47% sensitivity (95% CI 33%-61%). In studies comparing ultrasound with vs without AFP measurement, ultrasound detected any stage HCC with a lower level of sensitivity than ultrasound plus AFP measurement (relative risk [RR] 0.88; 95% CI 0.83-0.93) and early-stage HCC with a lower level of sensitivity than ultrasound plus AFP measurement (RR 0.81; 95% CI 0.71-0.93). However, ultrasound alone detected HCC with a higher level of specificity than ultrasound plus AFP measurement (RR 1.08; 95% CI 1.05-1.09). Ultrasound with vs without AFP detected early-stage HCC with 63% sensitivity (95% CI 48%-75%) and 45% sensitivity (95% CI 30%-62%), respectively (P = .002). Only 4 studies evaluated computed tomography or magnetic resonance image-based surveillance, which detected HCC with 84% sensitivity (95% CI 70%-92%).
Conclusions: We found ultrasound alone has a low sensitivity to detect early stage HCC in patients with cirrhosis. Addition of AFP to ultrasound significantly increases sensitivity of early HCC detection in clinical practice.
Keywords: Alpha Fetoprotein; Liver Cancer; Screening; Ultrasound.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Why Won't the Alpha-fetoprotein Test Go Gentle Into the Good Night?Gastroenterology. 2018 May;154(6):1572-1573. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.03.037. Epub 2018 Mar 28. Gastroenterology. 2018. PMID: 29601826 No abstract available.
-
Surveillance for Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Ultrasound Plus Alpha-Fetoprotein Measurement: More Details, More Significance.Gastroenterology. 2018 Oct;155(4):1274-1275. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.03.071. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Gastroenterology. 2018. PMID: 30227109 No abstract available.
-
Reply.Gastroenterology. 2018 Oct;155(4):1275-1276. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.09.026. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Gastroenterology. 2018. PMID: 30236560 No abstract available.
-
Historical Data Are Not Relevant to the Diagnostic Performance of Ultrasound in Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Gastroenterology. 2019 Sep;157(3):899-900. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.12.051. Epub 2019 May 17. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 31108052 No abstract available.
-
Reply.Gastroenterology. 2019 Sep;157(3):901-902. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.011. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 31306633 No abstract available.
References
-
- Llovet JM, Fuster J, Bruix J. Intention-to-treat analysis of surgical treatment for early hepatocellular carcinoma: resection versus transplantation. Hepatology. 1999;30:1434–40. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A, Schwartz M, Porta C, Zeuzem S, Bolondi L, Greten TF, Galle PR, Seitz JF, Borbath I, Haussinger D, Giannaris T, Shan M, Moscovici M, Voliotis D, Bruix J. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:378–90. - PubMed
-
- Kansagara D, Papak J, Pasha AS, O’Neil M, Freeman M, Relevo R, Quinones A, Motu’apuaka M, Jou JH. Screening for hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic liver disease: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2014;161:261–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

