Brief Report: The Genetic Profile of Rheumatoid Factor-Positive Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Resembles That of Adult Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 29426059
- PMCID: PMC5984672
- DOI: 10.1002/art.40443
Brief Report: The Genetic Profile of Rheumatoid Factor-Positive Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Resembles That of Adult Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
Objective: Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) comprises 7 heterogeneous categories of chronic childhood arthritides. Approximately 5% of children with JIA have rheumatoid factor (RF)-positive arthritis, which phenotypically resembles adult rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Our objective was to compare and contrast the genetics of RF-positive polyarticular JIA with those of RA and selected other JIA categories, to more fully understand the pathophysiologic relationships of inflammatory arthropathies.
Methods: Patients with RF-positive polyarticular JIA (n = 340) and controls (n = 14,412) were genotyped using the Immunochip array. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms were tested for association using a logistic regression model adjusting for admixture proportions. We calculated weighted genetic risk scores (wGRS) of reported RA and JIA risk loci, and we compared the ability of these wGRS to predict RF-positive polyarticular JIA.
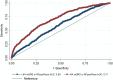
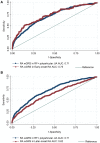
Results: As expected, the HLA region was strongly associated with RF-positive polyarticular JIA (P = 5.51 × 10-31 ). Nineteen of 44 RA risk loci and 6 of 27 oligoarticular/RF-negative polyarticular JIA risk loci were associated with RF-positive polyarticular JIA (P < 0.05). The RA wGRS predicted RF-positive polyarticular JIA (area under the curve [AUC] 0.71) better than did the oligoarticular/RF-negative polyarticular JIA wGRS (AUC 0.59). The genetic profile of patients with RF-positive polyarticular JIA was more similar to that of RA patients with age at onset 16-29 years than to that of RA patients with age at onset ≥70 years.
Conclusion: RF-positive polyarticular JIA is genetically more similar to adult RA than to the most common JIA categories and thus appears to be a childhood-onset presentation of autoantibody-positive RA. These findings suggest common disease mechanisms, which could lead to novel therapeutic targets and shared treatment strategies.
© 2018 The Authors. Arthritis & Rheumatology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Genetics: Subtype of JIA is genetically similar to adult RA.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018 Mar 21;14(4):181. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2018.30. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29559712 No abstract available.
References
-
- Petty RE, Southwood TR, Manners P, Baum J, Glass DN, Goldenberg J, et al. International League of Associations for Rheumatology classification of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: second revision, Edmonton, 2001. J Rheumatol 2004;31:390–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RP-PG-0310-1002/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- 20542/ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 DK062413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR060893/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062432/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- FRN-82517/CIHR/Canada
- U01 GM092691/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062422/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AR048929/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR063759/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067677/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 076113/C/04/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 AR057106/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA141743/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 AR058587/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI082714/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM103510/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 20542/VAC_/Versus Arthritis/United Kingdom
- G0000934/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U24 DK062429/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR053483/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 20385/ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- N01 AR062277/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062429/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 068545/Z/01/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- K23 AR050177/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062418/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR073750/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 AR059092/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR070549/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01 DK062423/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI067150/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MR/R013926/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 AR047363/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- MR/M004600/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01 AR042272/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 20164/ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 DK062420/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062431/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

