Impaired fear extinction in serotonin transporter knockout rats is associated with increased 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in the amygdala
- PMID: 29427306
- PMCID: PMC6120487
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.12822
Impaired fear extinction in serotonin transporter knockout rats is associated with increased 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in the amygdala
Abstract
Aims: One potential risk factor for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) involves the low activity (short; s) allelic variant of the serotonin transporter-linked polymorphic region (5-HTTLPR), possibly due to reduced prefrontal control over the amygdala. Evidence shows that DNA methylation/demethylation is crucial for fear extinction in these brain areas and is associated with neuronal activation marker c-Fos expression. We hypothesized that impaired fear extinction in serotonin transporter knockout (5-HTT-/- ) rats is related to changes in DNA (de) methylation and c-Fos expression in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) and/or amygdala.
Methods: 5-HTT-/- and 5-HTT+/+ rats were subjected to fear extinction. 2 hours after the extinction session, the overall levels of DNA methylation (5-mC), demethylation (5-hmC), and c-Fos in fear extinction and nonfear extinction rats were measured by immunohistochemistry.
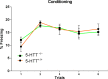
Results: 5-HTT-/- rats displayed decreased fear extinction. This was associated with reduced c-Fos activity in the infralimbic PFC. In the central nucleus of the amygdala, c-Fos immunoreactivity was increased in the fear extinction group compared to the no-fear extinction group, regardless of genotype. 5-hmC levels were unaltered in the PFC, but reduced in the amygdala of nonextinction 5-HTT-/- rats compared to nonextinction wild-type rats, which caught up to wild-type levels during fear extinction. 5-mC levels were stable in central amygdala in both wild-type and 5-HTT-/- extinction rats. Finally, c-Fos and 5-mC levels were correlated with the prelimbic PFC, but not amygdala.
Conclusions: In the amygdala, DNA demethylation, independent from c-Fos activation, may contribute to individual differences in risk for PTSD, as conferred by the 5-HTTLPR s-allele.
Keywords: 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC); 5-methylcytosine (5-mC); DNA (de) methylation; epigenetics; fear extinction; serotonin transporter knockout.
© 2018 The Authors. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Impaired stress-coping and fear extinction and abnormal corticolimbic morphology in serotonin transporter knock-out mice.J Neurosci. 2007 Jan 17;27(3):684-91. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4595-06.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17234600 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Histone Acetylation in the Infralimbic Prefrontal Cortex is Associated with Fear Extinction.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Oct;37(7):1287-1301. doi: 10.1007/s10571-017-0464-6. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 28097489 Free PMC article.
-
Social defeat: impact on fear extinction and amygdala-prefrontal cortical theta synchrony in 5-HTT deficient mice.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22600. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022600. Epub 2011 Jul 27. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21818344 Free PMC article.
-
Acute inescapable stress alleviates fear extinction recall deficits caused by serotonin transporter abolishment.Behav Brain Res. 2018 Jul 2;346:16-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2017.12.009. Epub 2017 Dec 9. Behav Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29233642
-
Behavioural therapy based on distraction alleviates impaired fear extinction in male serotonin transporter knockout rats.J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2012 Jul;37(4):224-30. doi: 10.1503/jpn.110116. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22353635 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Fear Extinction and Predictive Trait-Like Inter-Individual Differences in Rats Lacking the Serotonin Transporter.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 30;22(13):7088. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137088. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34209318 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired Fear Extinction Recall in Serotonin Transporter Knockout Rats Is Transiently Alleviated during Adolescence.Brain Sci. 2019 May 22;9(5):118. doi: 10.3390/brainsci9050118. Brain Sci. 2019. PMID: 31121975 Free PMC article.
-
The association between serotonin transporter availability and the neural correlates of fear bradycardia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Dec 17;116(51):25941-25947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1904843116. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31772023 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the serotonin transporter in prefrontal cortex glutamatergic signaling following short- and long-access cocaine self-administration.Addict Biol. 2021 Mar;26(2):e12896. doi: 10.1111/adb.12896. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Addict Biol. 2021. PMID: 32187792 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potentials of natural products for post-traumatic stress disorder: A focus on epigenetics.Chin Herb Med. 2024 Jul 22;17(2):203-219. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2024.07.004. eCollection 2025 Apr. Chin Herb Med. 2024. PMID: 40256720 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gillies D, Taylor F, Gray C, et al. Psychological therapies for the treatment of post‐traumatic stress disorder in children and adolescents. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012; 12: CD006726. - PubMed
-
- Gressier F, Calati R, Balestri M, et al. The 5‐HTTLPR polymorphism and posttraumatic stress disorder: a meta‐analysis. J Trauma Stress. 2013;26:645‐653. - PubMed
-
- Lonsdorf TB, Weike AI, Nikamo P, et al. Genetic gating of human fear learning and extinction: possible implications for gene‐environment interaction in anxiety disorder. Psychol Sci. 2009;20:198‐206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

