Treatment of hepatitis C virus infection with direct-acting antiviral agents: 100% cure?
- PMID: 29427484
- PMCID: PMC7713514
- DOI: 10.1111/liv.13673
Treatment of hepatitis C virus infection with direct-acting antiviral agents: 100% cure?
Abstract
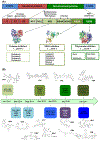
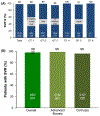
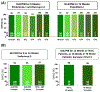
Around 71 million people are chronically infected with HCV worldwide. HCV antiviral drug development has been remarkable. The availability of pangenotypic direct-acting antivirals with excellent efficacy and good tolerability profiles offer a unique opportunity to achieve HCV elimination worldwide. IFN-free DAA combinations can now cure HCV in more than 95% of patients with HCV infection after 8-12 weeks of treatment. Programmes to eliminate HCV must include increased screening (risk-based and universal), linkage to care, as well as increased access to treatment worldwide. In this paper, we will review the available data on recently approved direct-acting antiviral agents, with sustained virological response that reaches almost 100%.
Keywords: HCV elimination; chronic hepatitis C; compliance; genotype; people who inject drugs; screening.
© 2018 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
Tarik Asselah is a speaker and investigator for AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Gilead, Roche and Merck. Patrick Marcellin is a speaker for AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Gilead, Roche and Merck. Raymond Schinazi is the founder and major shareholder of Cocrystal Pharma, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Asselah T, Boyer N, Saadoun D, et al. Direct-acting antivirals for the treatment of hepatitis C virus infection: optimizing current IFN-free treatment and future perspectives. Liver Int. 2016;36(Suppl 1):47–57. - PubMed
-
- Martinot-Peignoux M, Stern C, Maylin S, et al. Twelve weeks post treatment follow-up is as relevant as 24 weeks to determine the sustained virologic response in patients with hepatitis C virus receiving pegylated interferon and ribavirin. Hepatology. 2010;51:1122–1126. - PubMed
-
- Maylin S, Martinot-Peignoux M, Moucari R, et al. Eradication of hepatitis C virus in patients successfully treated for chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:821–829. - PubMed
-
- Afdhal N, Everson GT, Calleja JL, et al. Effect of viral suppression on hepaticvenous pressure gradient in hepatitis C with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. J Viral Hepat. 2017;24:823–831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

