The Neurotropic Properties of AAV-PHP.B Are Limited to C57BL/6J Mice
- PMID: 29428298
- PMCID: PMC5911151
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.01.018
The Neurotropic Properties of AAV-PHP.B Are Limited to C57BL/6J Mice
Abstract
Improved delivery of adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors to the CNS will greatly enhance their clinical utility. Selection of AAV9 variants in a mouse model led to the isolation of a capsid called PHP.B, which resulted in remarkable transduction of the CNS following intravenous infusion. However, we now show here that this enhanced CNS tropism is restricted to the model in which it was selected, i.e., a Cre transgenic mouse in a C57BL/6J background, and was not found in nonhuman primates or the other commonly used mouse strain BALB/cJ. We also report the potential for serious acute toxicity in NHP after systemic administration of high dose of AAV.
Copyright © 2018 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
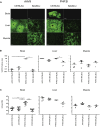
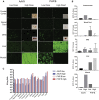
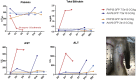
Comment in
-
Safety First: Perspective on Patient-Centered Development of AAV Gene Therapy Products.Mol Ther. 2018 Mar 7;26(3):669-671. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.02.009. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Mol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29503193 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Gao G., Vandenberghe L.H., Wilson J.M. New recombinant serotypes of AAV vectors. Curr. Gene Ther. 2005;5:285–297. - PubMed
-
- Pacak C.A., Mah C.S., Thattaliyath B.D., Conlon T.J., Lewis M.A., Cloutier D.E., Zolotukhin I., Tarantal A.F., Byrne B.J. Recombinant adeno-associated virus serotype 9 leads to preferential cardiac transduction in vivo. Circ. Res. 2006;99:e3–e9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

