Hearing Impairment, Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Dementia: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies
- PMID: 29430246
- PMCID: PMC5806170
- DOI: 10.1159/000485178
Hearing Impairment, Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Dementia: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies
Abstract
Background: To estimate a pooled association between hearing impairment and risk of mild cognitive impairment and dementia.
Methods: PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science were searched for prospective cohort studies that examined the association between hearing impairment and risk of mild cognitive impairment and/or dementia. Random-effects models were fitted to estimate the summary risk ratios (RRs) and 95% confidence interval (CIs), which represents the pooled association between hearing impairment with risk of mild cognitive impairment and dementia, compared to subjects free of hearing impairment.
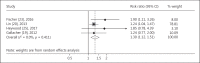
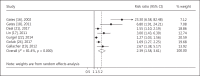
Results: Four studies on hearing impairment with mild cognitive impairment and 7 studies on hearing impairment with dementia were included in the meta-analysis. A total of 15,521 subjects were studied with follow-up periods between 2 and 16.8 years. Hearing impairment was associated with a greater risk of mild cognitive impairment (RR = 1.30, 95% CI: 1.12, 1.51) and dementia (RR = 2.39, 95% CI: 1.58, 3.61).
Conclusions: The meta-analysis showed that hearing impairment is associated with a higher risk of mild cognitive impairment and dementia among older adults.
Keywords: Dementia; Hearing impairment; Meta-analysis; Mild cognitive impairment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of Age-Related Hearing Loss With Cognitive Function, Cognitive Impairment, and Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Feb 1;144(2):115-126. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2017.2513. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018. PMID: 29222544 Free PMC article.
-
The Association between Vision Impairment and Incidence of Dementia and Cognitive Impairment: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Ophthalmology. 2021 Aug;128(8):1135-1149. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2020.12.029. Epub 2021 Jan 8. Ophthalmology. 2021. PMID: 33422559
-
Association of age-related hearing loss with cognitive impairment and dementia: an umbrella review.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Sep 18;15:1241224. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1241224. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37790283 Free PMC article.
-
Aspirin Use on Incident Dementia and Mild Cognitive Decline: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Feb 4;12:578071. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.578071. eCollection 2020. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33613260 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of frailty, mild cognitive impairment and cognitive frailty on adverse health outcomes among community-dwelling older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 31;9:1009794. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1009794. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36388900 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association Between Hearing and Vision Impairment and Risk of Dementia: Results of a Case-Control Study Based on Secondary Data.Front Aging Neurosci. 2019 Dec 20;11:363. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00363. eCollection 2019. Front Aging Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31920631 Free PMC article.
-
National Survey of Pharmacist Awareness, Interest, and Readiness for Over-the-Counter Hearing Aids.Pharmacy (Basel). 2022 Nov 12;10(6):150. doi: 10.3390/pharmacy10060150. Pharmacy (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36412826 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related Changes in Neural Coding of Envelope Cues: Peripheral Declines and Central Compensation.Neuroscience. 2019 May 21;407:21-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.12.007. Epub 2018 Dec 14. Neuroscience. 2019. PMID: 30553793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes on clinical and participatory outcomes in people with severe-to-profound hearing loss after cochlear implantation: protocol of a multicentre prospective observational cohort study - Societal Merit of Intervention on Hearing Loss Evaluation (SMILE).BMJ Open. 2023 Jun 27;13(6):e072689. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-072689. BMJ Open. 2023. PMID: 37369408 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the genetic relationship between hearing impairment and Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2020 Sep 25;12(1):e12108. doi: 10.1002/dad2.12108. eCollection 2020. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2020. PMID: 33005726 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seshadri S, Wolf PA, Beiser A, Au R, McNulty K, White R, D'Agostino RB. Lifetime risk of dementia and Alzheimer's disease. The impact of mortality on risk estimates in the Framingham Study. Neurology. 1997;49:1498–1504. - PubMed
-
- Prince M, Guerchet M, Prina M. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015. The Epidemiology and Impact of Dementia: Current State and Future Trends.
-
- Alzheimer's Association 2017 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimer Dementia. 2017;13:325–373. - PubMed
-
- Sachdev PS, Lipnicki DM, Kochan NA, Crawford JD, Thalamuthu A, Andrews G, Brayne C, Matthews FE, Stephan BC, Lipton RB, Katz MJ, Ritchie K, Carriere I, Ancelin ML, Lam LC, Wong CH, Fung AW, Guaita A, Vaccaro R, Davin A, Ganguli M, Dodge H, Hughes T, Anstey KJ, Cherbuin N, Butterworth P, Ng TP, Gao Q, Reppermund S, Brodaty H, Schupf N, Manly J, Stern Y, Lobo A, Lopez-Anton R, Santabarbara J. The prevalence of mild cognitive impairment in diverse geographical and ethnocultural regions: The COSMIC Collaboration. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0142388. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources