Optimisation of culture composition for glyphosate degradation by Burkholderia vietnamiensis strain AQ5-12
- PMID: 29430369
- PMCID: PMC5794677
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-018-1123-4
Optimisation of culture composition for glyphosate degradation by Burkholderia vietnamiensis strain AQ5-12
Abstract
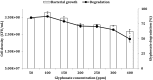
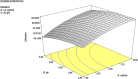
The herbicide glyphosate is often used to control weeds in agricultural lands. However, despite its ability to effectively kill weeds at low cost, health problems are still reported due to its toxicity level. The removal of glyphosate from the environment is usually done by microbiological process since chemical process of degradation is ineffective due to the presence of highly stable bonds. Therefore, finding glyphosate-degrading microorganisms in the soil of interest is crucial to remediate this glyphosate. Burkholderia vietnamiensis strain AQ5-12 was found to have glyphosate-degrading ability. Optimisation of biodegradation condition was carried out utilising one factor at a time (OFAT) and response surface methodology (RSM). Five parameters including carbon and nitrogen source, pH, temperature and glyphosate concentration were optimised. Based on OFAT result, glyphosate degradation was observed to be optimum at fructose concentration of 6, 0.5 g/L ammonia sulphate, pH 6.5, temperature of 32 °C and glyphosate concentration at 100 ppm. Meanwhile, RSM resulted in a better degradation with 92.32% of 100 ppm glyphosate compared to OFAT. The bacterium was seen to tolerate up to 500 ppm glyphosate while increasing concentration results in reduced degradation and bacterial growth rate.
Keywords: Bioremediation; Burkholderia vietnamiensis; Glyphosate; One-factor-at-time (OFAT); Response surface methodology (RSM).
Figures









Similar articles
-
Isolation and optimization of a glyphosate-degrading Rhodococcus soli G41 for bioremediation.Arch Microbiol. 2022 Apr 12;204(5):252. doi: 10.1007/s00203-022-02875-0. Arch Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35411478
-
Statistical optimisation of growth conditions and diesel degradation by the Antarctic bacterium, Rhodococcus sp. strain AQ5‒07.Extremophiles. 2020 Mar;24(2):277-291. doi: 10.1007/s00792-019-01153-0. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Extremophiles. 2020. PMID: 31863235
-
Characterisation of the simultaneous molybdenum reduction and glyphosate degradation by Burkholderia vietnamiensis AQ5-12 and Burkholderia sp. AQ5-13.3 Biotech. 2018 Feb;8(2):117. doi: 10.1007/s13205-018-1141-2. Epub 2018 Feb 7. 3 Biotech. 2018. PMID: 29430378 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in glyphosate biodegradation.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Jun;102(12):5033-5043. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9035-0. Epub 2018 Apr 29. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29705962 Review.
-
Glyphosate Pollution Treatment and Microbial Degradation Alternatives, a Review.Microorganisms. 2021 Nov 10;9(11):2322. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9112322. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34835448 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation and optimization of a glyphosate-degrading Rhodococcus soli G41 for bioremediation.Arch Microbiol. 2022 Apr 12;204(5):252. doi: 10.1007/s00203-022-02875-0. Arch Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35411478
-
Microbiomes and glyphosate biodegradation in edaphic and aquatic environments: recent issues and trends.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Apr 28;38(6):98. doi: 10.1007/s11274-022-03281-w. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35478266 Review.
-
Analysis of the Genome of the Heavy Metal Resistant and Hydrocarbon-Degrading Rhizospheric Pseudomonas qingdaonensis ZCR6 Strain and Assessment of Its Plant-Growth-Promoting Traits.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 25;23(1):214. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010214. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008639 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical optimisation of growth conditions and diesel degradation by the Antarctic bacterium, Rhodococcus sp. strain AQ5‒07.Extremophiles. 2020 Mar;24(2):277-291. doi: 10.1007/s00792-019-01153-0. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Extremophiles. 2020. PMID: 31863235
-
Manganese Removal Using Functionalised Thiosalicylate-Based Ionic Liquid: Water Filtration System Application.Molecules. 2023 Jul 31;28(15):5777. doi: 10.3390/molecules28155777. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37570745 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benslama O, Boulahrouf A. Isolation and characterization of glyphosate-degrading bacteria from different soils of Algeria. Afr J Microbiol Res. 2013;7:5587–5595. doi: 10.5897/AJMR2013.6080. - DOI
-
- Boyd CE, Massaut L. Risks associated with the use of chemicals in pond aquaculture. Aquac Eng. 1999;20:113–132. doi: 10.1016/S0144-8609(99)00010-2. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

