The global epidemiology of adolescents living with HIV: time for more granular data to improve adolescent health outcomes
- PMID: 29432227
- PMCID: PMC5929160
- DOI: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000449
The global epidemiology of adolescents living with HIV: time for more granular data to improve adolescent health outcomes
Abstract
Purpose of review: The aim of this study was to summarize recent evidence on the global epidemiology of adolescents (age 10-19 years) living with HIV (ALHIV), the burden of HIV on the health of adolescents and HIV-associated mortality.
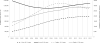
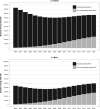
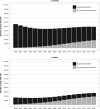
Recent findings: In 2016, there were an estimated 2.1 million (uncertainty bound 1.4-2.7 million) ALHIV; 770 000 younger (age 10-14 years) and 1.03 million older (age 15-19 years) ALHIV, 84% living in sub-Saharan Africa. The population of ALHIV is increasing, as more peri/postnatally infected ALHIV survive into older ages; an estimated 35% of older female ALHIV were peri/postnatally infected, compared with 57% of older male ALHIV. Although the numbers of younger ALHIV deaths are declining, deaths among older ALHIV have remained static since peaking in 2012. In 2015, HIV-associated mortality was the eighth leading cause of adolescent death globally and the fourth leading cause in African low and middle-income countries.
Summary: Needed investments into characterizing and improving adolescent HIV-related health outcomes include strengthening systems for nationally and globally disaggregated data by age, sex and mode of infection; collecting more granular data within routine programmes to identify structural, social and mental health challenges to accessing testing and care; and prioritizing viral load monitoring and adolescent-focused differentiated models of care.
Conflict of interest statement
ALS has no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Health for the world's adolescents: a second chance in the second decade. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2014. [cited 2017 January 06]. Available from: http://apps.who.int/adolescent/second-decade/files/1612_MNCAH_HWA_Execut....
-
- UNAIDS. [cited 2017 November 17];UNAIDS 2017 Estimates. 2017 Available from: http://aidsinfo.unaids.org/. Publicly available resource of UNAIDS estimates for key HIV indicators at regional, national and global levels.
-
- Slogrove AL, Mahy M, Armstrong A, Davies MA. Living and dying to be counted: What we know about the epidemiology of the global adolescent HIV epidemic. J Int AIDS Soc. 2017;20(Suppl 3):4–15. This review summarized nationally-representative population-based survey prevalence data on adolescents living with HIV in the 15 highest adolescent HIV burden countries in 2016 and describes helpful examples of national case-based surveillance systems including adolescents living with HIV. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

