Macromolecular prodrugs of ribavirin: Polymer backbone defines blood safety, drug release, and efficacy of anti-inflammatory effects
- PMID: 29432822
- PMCID: PMC7114659
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.02.012
Macromolecular prodrugs of ribavirin: Polymer backbone defines blood safety, drug release, and efficacy of anti-inflammatory effects
Abstract
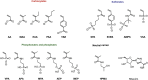
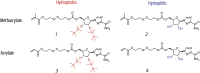
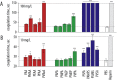
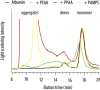
Macromolecular (pro)drugs hold much promise as broad-spectrum antiviral agents as either microbicides or carriers for intracellular delivery of antiviral drugs. Intriguing opportunity exists in combining the two modes of antiviral activity in the same polymer structure such that the same polymer acts as a microbicide and also serves to deliver the conjugated drug (ribavirin) into the cells. We explore this opportunity in detail and focus on the polymer backbone as a decisive constituent of such formulations. Fourteen polyanions (polycarboxylates, polyphosphates and polyphosphonates, and polysulfonates) were analyzed for blood pro/anti coagulation effects, albumin binding and albumin aggregation, inhibitory activity on polymerases, cytotoxicity, and anti-inflammatory activity in stimulated macrophages. Ribavirin containing monomers were designed to accommodate the synthesis of macromolecular prodrugs with disulfide-exchange triggered drug release. Kinetics of drug release was fast in all cases however enhanced hydrophobicity of the polymer significantly slowed release of ribavirin. Results of this study present a comprehensive view on polyanions as backbone for macromolecular prodrugs of ribavirin as broad-spectrum antiviral agents.
Keywords: Albumin; Antiviral; Drug release; Macrmolecular prodrug.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Macromolecular Prodrugs of Ribavirin: Structure-Function Correlation as Inhibitors of Influenza Infectivity.Mol Pharm. 2017 Jan 3;14(1):234-241. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.6b00826. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Mol Pharm. 2017. PMID: 28043136
-
Macromolecular prodrugs of ribavirin: concerted efforts of the carrier and the drug.Adv Healthc Mater. 2014 Sep;3(9):1404-7. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201300637. Epub 2014 Jan 10. Adv Healthc Mater. 2014. PMID: 24408515
-
Macromolecular (pro)drugs with concurrent direct activity against the hepatitis C virus and inflammation.J Control Release. 2014 Dec 28;196:197-207. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.09.032. Epub 2014 Oct 16. J Control Release. 2014. PMID: 25451544
-
Strategies for ribavirin prodrugs and delivery systems for reducing the side-effect hemolysis and enhancing their therapeutic effect.J Control Release. 2015 Jul 10;209:27-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.04.016. Epub 2015 Apr 14. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 25883028 Review.
-
Stimuli-sensitive polymer prodrug nanocarriers by reversible-deactivation radical polymerization.Chem Soc Rev. 2024 Jun 17;53(12):6511-6567. doi: 10.1039/d2cs01060g. Chem Soc Rev. 2024. PMID: 38775004 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In situ cellular hitchhiking of nanoparticles for drug delivery.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2024 Jan;204:115143. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2023.115143. Epub 2023 Nov 24. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2024. PMID: 38008185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Agents Based on Multivalent Inhibitors of Viral Infectivity.Adv Healthc Mater. 2021 Mar;10(6):e2001433. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202001433. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021. PMID: 33491915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward the prevention of coronavirus infection: what role can polymers play?Mater Today Adv. 2021 Jun;10:100140. doi: 10.1016/j.mtadv.2021.100140. Epub 2021 Mar 20. Mater Today Adv. 2021. PMID: 33778467 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

