Regulation of Phosphorylation of AMPA Glutamate Receptors by Muscarinic M4 Receptors in the Striatum In vivo
- PMID: 29432883
- PMCID: PMC5851863
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.01.063
Regulation of Phosphorylation of AMPA Glutamate Receptors by Muscarinic M4 Receptors in the Striatum In vivo
Abstract
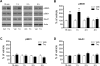
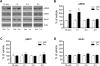
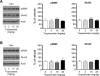
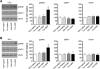
The acetylcholine muscarinic 4 (M4) receptor is a principal muscarinic receptor subtype present in the striatum. Notably, Gαi/o-coupled M4 receptors and Gαs/Golf-coupled dopamine D1 receptors are coexpressed in striatonigral projection neurons and are thought to interact with each other to regulate neuronal excitability, although underlying molecular mechanisms are poorly understood. In this study, we investigated the role of M4 receptors in the regulation of phosphorylation of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors in the rat normal and dopamine-stimulated striatum in vivo. We found that a systemic injection of a M4 antagonist tropicamide increased AMPA receptor GluA1 subunit phosphorylation at a protein kinase A-dependent site (S845) in the striatum. The tropicamide-induced S845 phosphorylation was rapid, reversible, and dose-dependent and occurred in the two subdivisions of the striatum, i.e., the caudate putamen and nucleus accumbens. Coadministration of subthreshold doses of tropicamide and a D1 agonist SKF81297 induced a significant increase in S845 phosphorylation. Coadministered tropicamide and a dopamine psychostimulant amphetamine at their subthreshold doses also elevated S845 phosphorylation. Tropicamide alone or coinjected with SKF81297 or amphetamine had no effect on GluA1 phosphorylation at S831. Tropicamide did not affect GluA2 phosphorylation at S880. These results reveal a selective inhibitory linkage from M4 receptors to GluA1 in S845 phosphorylation in striatal neurons. Blockade of the M4-mediated inhibition significantly augments constitutive and dopamine-stimulated GluA1 S845 phosphorylation.
Keywords: D1 receptor; D2 receptor; caudate putamen; muscarinic receptor; nucleus accumbens; protein kinase A.
Copyright © 2018 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aubert I, Ghorayeb I, Normand E, Bloch B. Phenotypical characterization of the neurons expressing the D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in the monkey striatum. J Comp Neurol. 2000;418:22–32. - PubMed
-
- Barria A, Derkach V, Soderling T. Identification of the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II regulatory phosphorylation site in the α-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate-type glutamate receptor. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:32727–32730. - PubMed
-
- Bernard V, Dumartin B, Lamy E, Bloch B. Fos immunoreactivity after stimulation or inhibition of muscarinic receptors indicates anatomical specificity for cholinergic control of striatal efferent neurons and cortical neurons in the rat. Eur J Neurosci. 1993;5:1218–1225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

