An international survey on hypoglycemia among insulin-treated type I and type II diabetes patients: Turkey cohort of the non-interventional IO HAT study
- PMID: 29433560
- PMCID: PMC5809967
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-018-0238-2
An international survey on hypoglycemia among insulin-treated type I and type II diabetes patients: Turkey cohort of the non-interventional IO HAT study
Abstract
Background: Limited real-world data are currently available on hypoglycemia in diabetes patients. The International Operations Hypoglycemia Assessment Tool (IO HAT) study was designed to estimate hypoglycemia in insulin-treated type I (T1DM) and type II (T2DM) diabetes mellitus patients from 9 countries. The data from Turkey cohort are presented here.
Methods: A non-interventional study to determine the hypoglycemia incidence, retrospectively and prospectively, in Turkish T1DM and T2DM patients using a 2-part self-assessment questionnaire.
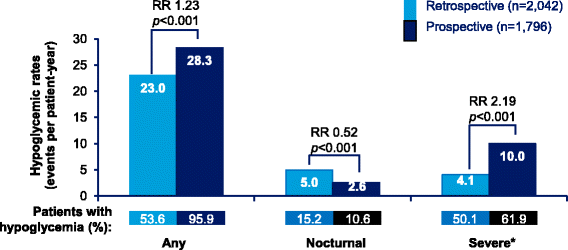
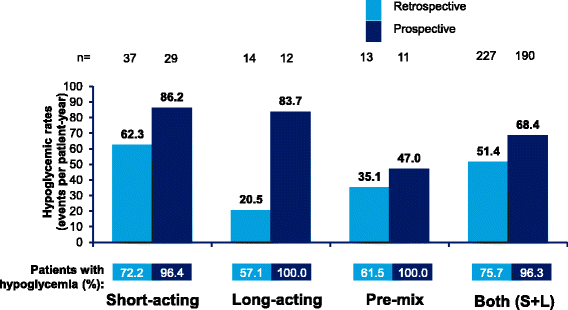
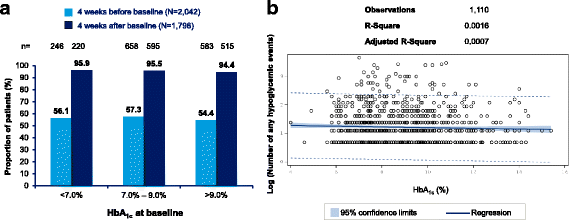
Results: Overall, 2348 patients were enrolled in the Turkey cohort (T1DM = 306 patients, T2DM = 2042 patients). In T1DM patients, 96.8% patients reported hypoglycemic events (Incidence rate [IR]: 68.6 events per patient-year [ppy]), prospectively, while 74.0% patients reported hypoglycemic events (IR: 51.7 events ppy), retrospectively. In T2DM patients, 95.9% patients (IR: 28.3 events ppy) reported hypoglycemic events, prospectively, while 53.6% patients (IR: 23.0 events ppy) reported hypoglycemic events, retrospectively. Nearly all patients reported hypoglycemia during the prospective period.
Conclusions: This is a first patient-reported dataset on hypoglycemia in Turkish, insulin-treated diabetes patients. A high incidence of patient-reported hypoglycemia confirms that hypoglycemia remains under-estimated. Hypoglycemia increased healthcare utilization impacting patients' quality of life. Hypoglycemia remains a common side effect with insulin-treatment and strategies to optimize therapy and reduce hypoglycemia occurrence in diabetes patients are required.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov, NCT02306681 (Date of registration: 12 Nov 2014; retrospectively registered).
Keywords: Diabetes; Hypoglycemia; IO HAT; Insulin; Non-interventional; Turkey.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Istanbul University Cerrahpasa Medical Faculty Clinical Trial Ethics Committee (Nb:83,045,809/604.01/02-42,378) approved this study. All patients provided written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
RE: Speaker fees from Novo Nordisk, MSD, AstraZeneca, Boehringer, Sanofi; participation in advisory boards from Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, AstraZeneca.
TT: Speaker fees from Gen Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Lilly, Novo Nordisk, MSD, AstraZeneca, Boehringer, Sanofi, Bilim; participation in advisory boards from Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Lilly.
IS: Speaker fees from Novo Nordisk, MSD, AstraZeneca, Boehringer, Sanofi, Lilly and Novartis; participation in advisory boards from Sanofi, Lilly, Novo Nordisk and AstraZeneca.
RS: Speaker fees from Novo Nordisk, MSD, AstraZeneca, Boehringer, Sanofi, Lilly, Novartis; participation in advisory boards from Sanofi, AstraZeneca.
AK: Speaker fees from Novo Nordisk, AstraZeneca, Boehringer, Sanofi, Lilly, Novartis; participation in advisory boards from Sanofi, AstraZeneca, NovoNordisk.
IY: Speaker fees from Novo Nordisk, AstraZeneca, Boehringer, Sanofi, Novartis, Lilly; participation in advisory boards from Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, AstraZeneca.
SC: Employee of Novo Nordisk.
NT: Speaker fees from Novo Nordisk, MSD, AstraZeneca, Boehringer, Sanofi, Novartis, Lilly; participation in advisory boards from Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, AstraZeneca.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures





References
-
- Gumprecht J, Nabrdalik K. Hypoglycemia in patients with insulin-treated diabetes. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2016;126(11):870–878. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

