Ipilimumab induced digital vasculitis
- PMID: 29433584
- PMCID: PMC5809839
- DOI: 10.1186/s40425-018-0321-2
Ipilimumab induced digital vasculitis
Abstract
Background: Immune check point inhibitors (ICIs) have emerged as a new therapeutic paradigm for a variety of malignancies including metastatic melanoma. As the use of ICIs expand, immune-mediated adverse events are becoming a common occurrence.
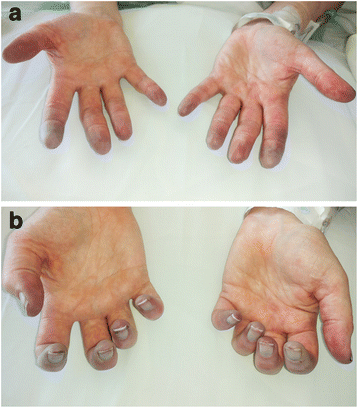
Case presentation: We describe the first reported patient with small vessel vasculitis, manifested by digital ischemia, following treatment with high dose Ipilimumab for resected stage IIIB/C melanoma. This patient received high dose steroids, five-day intravenous (IV) Epoprostenol protocol, botulinum toxin injections, and Rituximab 375 mg/m2 weekly for four cycles. With this treatment regimen, the digital ischemia did not progress proximally, but she did require multiple distal digit amputations about six months after the onset of her symptoms.
Conclusions: Prompt identification and management of immune related adverse events (IRAEs) are critical to optimal patient management. This patient's vasculitis did not reverse, but was likely halted and stabilized with multiple immunosuppressive medications.
Keywords: Immune related adverse events (IRAEs); Ipilimumab; Vasculitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
No formal ethics approval was needed since we were only reporting an observational case report. Consent was obtained from the patient.
Consent for publication
Consent was obtained from the patient. She signed a biomed generic consent for this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


Comment in
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related acral vasculitis.J Immunother Cancer. 2018 Nov 16;6(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s40425-018-0443-6. J Immunother Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30446009 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Skin cancers. (Accessed 1 May 2017, at http://www.who.int/uv/faq/skincancer/en/index1.html.)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
