Polo-like kinase 4 inhibition produces polyploidy and apoptotic death of lung cancers
- PMID: 29434041
- PMCID: PMC5828621
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1719760115
Polo-like kinase 4 inhibition produces polyploidy and apoptotic death of lung cancers
Abstract
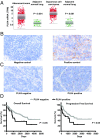
Polo-like kinase 4 (PLK4) is a serine/threonine kinase regulating centriole duplication. CFI-400945 is a highly selective PLK4 inhibitor that deregulates centriole duplication, causing mitotic defects and death of aneuploid cancers. Prior work was substantially extended by showing CFI-400945 causes polyploidy, growth inhibition, and apoptotic death of murine and human lung cancer cells, despite expression of mutated KRAS or p53. Analysis of DNA content by propidium iodide (PI) staining revealed cells with >4N DNA content (polyploidy) markedly increased after CFI-400945 treatment. Centrosome numbers and mitotic spindles were scored. CFI-400945 treatment produced supernumerary centrosomes and mitotic defects in lung cancer cells. In vivo antineoplastic activity of CFI-400945 was established in mice with syngeneic lung cancer xenografts. Lung tumor growth was significantly inhibited at well-tolerated dosages. Phosphohistone H3 staining of resected lung cancers following CFI-400945 treatment confirmed the presence of aberrant mitosis. PLK4 expression profiles in human lung cancers were explored using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and RNA in situ hybridization (RNA ISH) of microarrays containing normal and malignant lung tissues. PLK4 expression was significantly higher in the malignant versus normal lung and conferred an unfavorable survival (P < 0.05). Intriguingly, cyclin dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) antagonism cooperated with PLK4 inhibition. Taken together, PLK4 inhibition alone or as part of a combination regimen is a promising way to combat lung cancer.
Keywords: CFI-400945; PLK4 inhibitor; centriole duplication; lung cancer; polyploidy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Comment in
-
CFI-400945 is not a selective cellular PLK4 inhibitor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 13;115(46):E10808-E10809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1813310115. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30377272 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to Oegema et al.: CFI-400945 and Polo-like kinase 4 inhibition.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 13;115(46):E10810-E10811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1813967115. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30377273 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Torre LA, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Torre LA, Siegel RL, Ward EM, Jemal A. Global cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends–An update. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2016;25:16–27. - PubMed
-
- Torre LA, Siegel RL, Jemal A. Lung cancer statistics. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;893:1–19. - PubMed
-
- Bettencourt-Dias M, et al. SAK/PLK4 is required for centriole duplication and flagella development. Curr Biol. 2005;15:2199–2207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

