Transporter-Guided Delivery of Nanoparticles to Improve Drug Permeation across Cellular Barriers and Drug Exposure to Selective Cell Types
- PMID: 29434548
- PMCID: PMC5791163
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00027
Transporter-Guided Delivery of Nanoparticles to Improve Drug Permeation across Cellular Barriers and Drug Exposure to Selective Cell Types
Abstract
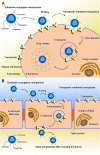
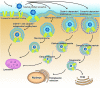
Targeted nano-drug delivery systems conjugated with specific ligands to target selective cell-surface receptors or transporters could enhance the efficacy of drug delivery and therapy. Transporters are expressed differentially on the cell-surface of different cell types, and also specific transporters are expressed at higher than normal levels in selective cell types under pathological conditions. They also play a key role in intestinal absorption, delivery via non-oral routes (e.g., pulmonary route and nasal route), and transfer across biological barriers (e.g., blood-brain barrier and blood-retinal barrier. As such, the cell-surface transporters represent ideal targets for nano-drug delivery systems to facilitate drug delivery to selective cell types under normal or pathological conditions and also to avoid off-target adverse side effects of the drugs. There is increasing evidence in recent years supporting the utility of cell-surface transporters in the field of nano-drug delivery to increase oral bioavailability, to improve transfer across the blood-brain barrier, and to enhance delivery of therapeutics in a cell-type selective manner in disease states. Here we provide a comprehensive review of recent advancements in this interesting and important area. We also highlight certain key aspects that need to be taken into account for optimal development of transporter-assisted nano-drug delivery systems.
Keywords: intestinal absorption; nano-drug delivery systems; nanoparticles; plasma membrane transporters; targeted drug delivery; transfer across blood–brain barrier.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

