TNF-α inhibits SATB2 expression and osteoblast differentiation through NF-κB and MAPK pathways
- PMID: 29435145
- PMCID: PMC5797016
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.23373
TNF-α inhibits SATB2 expression and osteoblast differentiation through NF-κB and MAPK pathways
Abstract
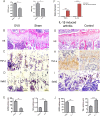
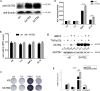
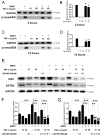
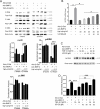
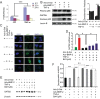
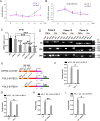
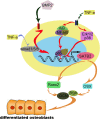
Although the mechanisms of Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) on facilitating osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption is well known, the mechanisms behind the suppression of the osteoblast differentiation from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are still poorly understood. In this study, we observed a negative correlation between TNF-α levels and the expression of special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 2 (SATB2), a critical osteoblastogenesis transcription factor, in ovariectomy (OVX)-induced bone loss and IL-1-induced arthritis animal model. We found that TNF-α treatment inhibited mesenchymal cell line C2C12 osteoblast differentiation and sharply decreased BMP2-induced SATB2 expression. Upon TNF-α treatment, the activity of smad1/5/8 was inhibited, by contrast, extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 (ERK1/2) and P38 was increased in C2C12 cells, the inhibitor of ERK1/2 (U0126) was found to abrogate the TNF-α inhibition of SATB2 expression. Furthermore, the NF-κB signaling pathway in C2C12 cells was significantly activated by the treatment of TNF-α, and TNF-α induced NF-κB directly binds to SATB2 promoter to suppress its expression. These results suggest that TNF-α suppresses SATB2 expression through activating NF-κB and MAPK signaling and depressing smad1/5/8 signaling, which contributes to the inhibition of osteoblast differentiation and might be potential therapeutic targets for inflammation-induced bone loss.
Keywords: SATB2 inhibition; TNF-α; inflammation-induced bone loss; osteoblast differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors have declared that no conflicts of interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pilose antler peptide potentiates osteoblast differentiation and inhibits osteoclastogenesis via manipulating the NF-κB pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Sep 16;491(2):388-395. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.07.091. Epub 2017 Jul 18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28733032
-
Simvastatin antagonizes tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibition of bone morphogenetic proteins-2-induced osteoblast differentiation by regulating Smad signaling and Ras/Rho-mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.J Endocrinol. 2008 Mar;196(3):601-13. doi: 10.1677/JOE-07-0532. J Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18310456
-
Gliotoxin potentiates osteoblast differentiation by inhibiting nuclear factor-κB signaling.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Jul;12(1):877-84. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3524. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25816130 Free PMC article.
-
Wrong place, wrong time: Runt-related transcription factor 2/SATB2 pathway in bone development and carcinogenesis.J Carcinog. 2021 Mar 25;20:2. doi: 10.4103/jcar.JCar_22_20. eCollection 2021. J Carcinog. 2021. PMID: 34211338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SATB2: A versatile transcriptional regulator of craniofacial and skeleton development, neurogenesis and tumorigenesis, and its applications in regenerative medicine.Genes Dis. 2020 Oct 17;9(1):95-107. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2020.10.003. eCollection 2022 Jan. Genes Dis. 2020. PMID: 35005110 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Osteoblast Differentiation by Cytokine Networks.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 11;22(6):2851. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062851. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33799644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TNF reduces osteogenic cell fate in PDL cells at transcriptional and functional levels without alteration of periodontal proliferative capacity.J Orofac Orthop. 2024 Aug 2. doi: 10.1007/s00056-024-00541-2. Online ahead of print. J Orofac Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39093345 English.
-
Role of the NF-kB signalling pathway in heterotopic ossification: biological and therapeutic significance.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Mar 4;22(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01533-w. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38439078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of the TNF-α/SATB2 axis in the induced apoptosis and inhibited autophagy of osteoblasts by the antipsychotic Risperidone.Mol Med. 2022 May 3;28(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00466-9. Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35505281 Free PMC article.
-
3D Cocultures of Osteoblasts and Staphylococcus aureus on Biomimetic Bone Scaffolds as a Tool to Investigate the Host-Pathogen Interface in Osteomyelitis.Pathogens. 2021 Jul 3;10(7):837. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10070837. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34357987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zaidi M. Skeletal remodeling in health and disease. Nat Med. 2007;13:791–801. - PubMed
-
- Xu J, Wu HF, Ang ES, Yip K, Woloszyn M, Zheng MH, Tan RX. NF-κB modulators in osteolytic bone diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009;20:7–17. - PubMed
-
- Gilbert L, He X, Farmer P, Rubin J, Drissi H, Van Wijnen AJ, Lian JB, Stein GS, Nanes MS. Expression of the osteoblast differentiation factor RUNX2 (Cbfa1/AML3/Pebp2αA) is inhibited by tumor necrosis factor-α. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:2695–2701. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

