The Pivotal Role of Imaging in TAVR Procedures
- PMID: 29435741
- PMCID: PMC5809539
- DOI: 10.1007/s11886-018-0949-z
The Pivotal Role of Imaging in TAVR Procedures
Abstract
Purpose of review: Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) is underpinned by an array of imaging techniques designed to not only select an appropriately sized implant but also to identify potential obstacles to procedural success. This review presents currently important aspects of TAVR imaging, describing the salient features of each modality as well as recent developments in the field.
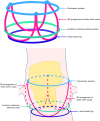
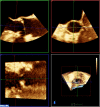
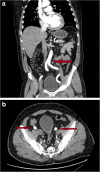
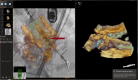
Recent findings: The latest data on TAVR outcomes reflects the increasing experience of operators and the significant role of pre-procedural imaging. Debate continues as to which modality sizes the aortic annulus most accurately, 3D transoesophageal echocardiography (TEE) or MDCT, as well as to whether the merits of real-time peri-procedural 3D imaging guidance outweigh the possible adverse consequences of general anaesthesia which is requisite for intraprocedural 3D TEE. TAVR is now largely based on pre-acquired roadmaps of the truncal vasculature and intense pre-procedural planning. TEE and Multi-detector computed tomography (MDCT) have been shown to perform similarly in annulus sizing. However, given the complexity of many TAVR patients and the importance of identifying the most suitable pathway to the valve as well as any potentially confounding other structural or functional heart disease, both modalities remain relevant in current TAVR.
Keywords: 3D transoesophageal echo; Aortic stenosis; Transcatheter aortic valve implantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest
C.B. and M.J.M. declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Khalique OK, Kodali SK, Paradis J-M, Nazif TM, Williams MR, Einstein AJ, et al. Aortic annular sizing using a novel 3-dimensional echocardiographic method: use and comparison with cardiac computed tomography. Circ: Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014;7(1):155–163. - PubMed
-
- Mehrotra P, Flynn AW, Jansen K, Tan TC, Mak G, Julien HM, et al. Differential left ventricular outflow tract remodeling and dynamics in aortic stenosis. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2015;28(11):1259–66. - PubMed
-
- Ng ACT, Delgado V, van der Kley F, Shanks M, van de Veire NRL, Bertini M, Nucifora G, van Bommel RJ, Tops LF, de Weger A, Tavilla G, de Roos A, Kroft LJ, Leung DY, Schuijf J, Schalij MJ, Bax JJ. Comparison of aortic root dimensions and geometries before and after transcatheter aortic valve implantation by 2- and 3-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography and multislice computed tomography. Circ: Cardiovasc Imaging. 2010;3(1):94–102. - PubMed
-
- Guez D, Boroumand G, Ruggiero NJ, Mehrotra P, Halpern EJ. Automated and manual measurements of the aortic annulus with ECG-gated cardiac CT angiography prior to transcatheter aortic valve replacement: comparison with 3D-transesophageal echocardiography. Acad Radiol. 2017;24(5):587–593. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2016.12.008. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

