Effects of bradykinin on TGF‑β1‑induced epithelial‑mesenchymal transition in ARPE‑19 cells
- PMID: 29436636
- PMCID: PMC5866033
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8556
Effects of bradykinin on TGF‑β1‑induced epithelial‑mesenchymal transition in ARPE‑19 cells
Abstract
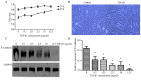
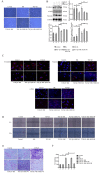
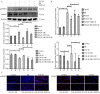
The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of bradykinin (BK) on an epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) model in retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells through exposure to transforming growth factor‑β1 (TGF‑β1). The aim was to improve the effect of BK on proliferative vitreoretinopathy (PVR) progression, and to find a novel method of clinical prevention and treatment for PVR. The morphology of ARPE‑19 cells was observed using an inverted phase‑contrast microscope. A Cell Counting Kit‑8 was used to assess the effects of TGF‑β1 on the proliferation of ARPE‑19 cells. Western blotting and immunofluorescence were used to detect the expression levels of the epithelial marker E‑cadherin, mesenchymal markers α‑smooth muscle actin (SMA) and vimentin, and phosphorylated (p) mothers against decapentaplegic homolog (Smad)3 and Smad7 of the TGF/Smad signaling pathway. Wound healing tests and Transwell assays were performed to detect cell migration ability. Reverse transcription‑quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT‑qPCR) analysis was performed to detect the expression levels of pSmad3 and Smad7 in the TGF/Smad signaling pathway. The results revealed that the addition of 10 ng/ml TGF‑β1 resulted in the expression of factors associated with EMT in ARPE‑19 cells. BK decreased the expression levels of the mesenchymal markers α‑SMA and vimentin, and increased the expression of the epithelial marker E‑cadherin. BK decreased cell migration in TGF‑β1‑induced EMT. These effects were reversed by HOE‑140, a specific BK 2 receptor antagonist. BK significantly downregulated the expression of pSmad3 and upregulated the expression of Smad7 in TGF‑β1‑treated ARPE‑19 cells, and the protective alterations produced by BK were inhibited by HOE‑140. In conclusion, 10 ng/ml TGF‑β1 resulted in EMT in ARPE‑19 cells and BK served a negative role in TGF‑β1‑induced EMT. BK had effects in TGF‑β1‑induced EMT by upregulating the expression of Smad7 and downregulating the expression of pSmad3 in TGF‑β/Smad signaling pathway, indicating that BK may be a novel and effective therapy for PVR.
Keywords: bradykinin; roliferative vitreoretinopathy; transforming growth factor-β1; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; retinal pigment epithelium.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

