Anticancer activity of caffeic acid n‑butyl ester against A431 skin carcinoma cell line occurs via induction of apoptosis and inhibition of the mTOR/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
- PMID: 29436638
- PMCID: PMC5866006
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8599
Anticancer activity of caffeic acid n‑butyl ester against A431 skin carcinoma cell line occurs via induction of apoptosis and inhibition of the mTOR/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway
Retraction in
-
[Retracted] Anticancer activity of caffeic acid n‑butyl ester against A431 skin carcinoma cell line occurs via induction of apoptosis and inhibition of the mTOR/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2021 May;23(5):372. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12011. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33760142 Free PMC article.
Abstract
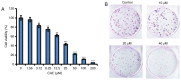
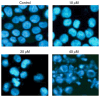
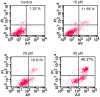
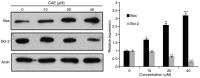
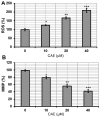
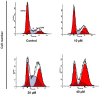
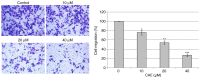
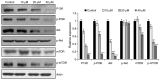
Skin cancer is one of the primary causes of mortality worldwide. With an increasing frequency of skin cancers, there is an urgent requirement for the development of numerous treatment options. The present study investigated the anticancer activity of caffeic acid n‑butyl ester (CAE) against the A431 skin cancer cell line. Antiproliferative effects were investigated using an MMT assay. Apoptosis was examined by DAPI and Annexin V/fluorescein isothiocyanate and propidium iodide staining. Reactive oxygen species (ROS), mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) and cell cycle analyses were performed via flow cytometry. Protein expression was determined by western blotting. The findings of the present study demonstrated that among a variety of cancer cell lines, CAE exhibited significant anticancer activity against the A431 skin cancer cell line with a half‑maximal inhibitory concentration of 20 µM. CAE was associated with apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of A431 cells, and induced ROS‑mediated alterations in MMP. In addition, CAE considerably suppressed the expression of some of the important proteins of the phosphoinositide 3‑kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT)/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) cascade. The results of the present study indicated that CAE exerted anticancer effects on the A431 skin carcinoma cell line via the induction of apoptosis and suppression of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Therefore, CAE may be beneficial for the development of chemotherapy for skin cancers.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

