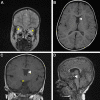
Nailing septo-optic dysplasia
- PMID: 29437724
- PMCID: PMC5836681
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2017-223956
Nailing septo-optic dysplasia
Keywords: neuroimaging; pituitary disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- De Morsier G. Études sur les dysraphiescranio-encephaliques: III. Agenesie duseptum lucidum avec malformation du tractusoptique: La dysplasiesepto-optique. Schweizer Arch Neurol Psychiatr 1956;77:267–92. - PubMed
-
- Webb EA, Dattani MT. Septo-optic dysplasia. Eur J Hum Genet 2010;18:393–7. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2009.125 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ulloa-Padilla JP, Izquierdo NJ, Oliver A. Increased intraocular pressure in a patient with septooptic dysplasia: a case report. J Glaucoma 2016;25:e713–7. doi:10.1097/IJG.0000000000000391 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
