Probiotic Properties of Exopolysaccharide-Producing Lactobacillus Strains Isolated from Tempoyak
- PMID: 29438288
- PMCID: PMC6017292
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23020398
Probiotic Properties of Exopolysaccharide-Producing Lactobacillus Strains Isolated from Tempoyak
Abstract
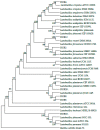
Tempoyak is a functional Malaysian food (an acid-fermented condiment) which is produced from the pulp of the durian (Durio zibethinus) fruit. The current study aimed to isolate and identify potential exopolysaccharide (EPS)-producing Lactobacillus strains from tempoyak for potential use as probiotics. Seven isolates (DUR2, DUR4, DUR5, DUR8, DUR12, DUR18, and DUR20) out of 44 were able to produce EPS, and exhibited resistance to acid and bile salt compared to the reference strains Lactobacillus rhmnosus (ATCC53103) and L. plantarum (ATCC8014). The seven isolated strains belonged to five different species-L. plantarum, L. fermentum, L. crispatus, L. reuteri, and L. pentosus-which were identified using API 50 CHL and 16S rRNA gene sequences (Polymerase chain reaction, PCR - based). The seven strains displayed different ability to produce EPS (100-850 mg/L). Isolates exhibited a high survivability to acid (pH 3.0), bile salts (0.3%), and gastrointestinal tract model (<70%). Results showed that the auto-aggregation and cell surface hydrophobicity ranged from 39.98% to 60.09% and 50.80% to 80.53%, respectively, whereas, the highest co-aggregation value (66.44%) was observed by L. fermentum (DUR8) with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The isolates showed good inhibitory activity against tested pathogens, high antioxidant activity (32.29% to 73.36%), and good ability to reduce cholesterol (22.55% to 75.15%). Thus, the seven tested strains have value as probiotics.
Keywords: Lactobacillus; antibacterial activity; exopolysaccharides; probiotics; tempoyak.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Day L., Seymour R.B., Pitts K.F., Konczak I., Lundin L. Incorporation of functional ingredients into foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2009;20:388–395. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2008.05.002. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

