Synthesis and Evaluation of the Tumor Cell Growth Inhibitory Potential of New Putative HSP90 Inhibitors
- PMID: 29438315
- PMCID: PMC6017909
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23020407
Synthesis and Evaluation of the Tumor Cell Growth Inhibitory Potential of New Putative HSP90 Inhibitors
Abstract
Background: Heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) is a well-known target for cancer therapy. In a previous work, some of us have reported a series of 3-aryl-naphtho[2,3-d]isoxazole-4,9-diones as inhibitors of HSP90.
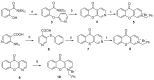
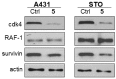
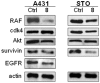
Methods: In the present work, various compounds with new chromenopyridinone and thiochromenopyridinone scaffolds were synthesized as potential HSP90 inhibitors. Their binding affinity to HSP90 was studied in vitro. Selected compounds (5 and 8) were further studied in various tumor cell lines regarding their potential to cause cell growth inhibition, alter the cell cycle profile, inhibit proliferation, and induce apoptosis. Their effect on HSP90 client protein levels was also confirmed in two cell lines. Finally, the antitumor activity of compound 8 was studied in A431 squamous cell carcinoma xenografts in nude mice.
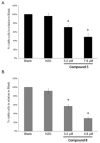
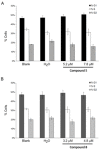
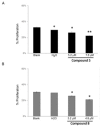
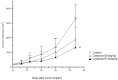
Results: Our results indicated that treatment with compounds 5 and 8 decreased the proliferation of tumor cell lines and compound 8 induced apoptosis. In addition, these two compounds were able to downregulate selected proteins known as "clients" of HSP90. Finally, treatment of xenografted mice with compound 5 resulted in a considerable dose-dependent inhibition of tumor growth.
Conclusions: Our results show that two new compounds with a chromenopyridinone and thiochromenopyridinone scaffold are promising putative HSP90 inhibitors causing tumor cell growth inhibition.
Keywords: (thio)chromenopyridinones; HSP90; antitumor; apoptosis; cell cycle; cell proliferation; naphthoquinones; tumor xenographs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
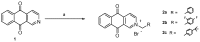
Similar articles
-
Antiproliferative effect of HSP90 inhibitor Y306zh against pancreatic cancer is mediated by interruption of AKT and MAPK signaling pathways.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2014;14(7):671-83. doi: 10.2174/1568009614666140908101523. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2014. PMID: 25219422
-
Isoxazolo(aza)naphthoquinones: a new class of cytotoxic Hsp90 inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2012 Jul;53:64-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.03.036. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Eur J Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22538015
-
CPUY201112, a novel synthetic small-molecule compound and inhibitor of heat shock protein Hsp90, induces p53-mediated apoptosis in MCF-7 cells.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 8;6:19004. doi: 10.1038/srep19004. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26743233 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in Hsp90 inhibitors as antitumor agents.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2008 Oct;8(7):761-82. doi: 10.2174/187152008785914824. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18855578 Review.
-
Heat shock proteins: a potential anticancer target.Curr Drug Targets. 2011 Dec;12(14):2001-8. doi: 10.2174/138945011798829339. Curr Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21777196 Review.
Cited by
-
Pirfenidone Sensitizes NCI-H460 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells to Paclitaxel and to a Combination of Paclitaxel with Carboplatin.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 26;23(7):3631. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073631. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35408988 Free PMC article.
-
BIRC3 and BIRC5: multi-faceted inhibitors in cancer.Cell Biosci. 2021 Jan 7;11(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13578-020-00521-0. Cell Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33413657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis of 2-amino-9H-chromeno[2,3-d]thiazol-9-ones with anti-inflammatory activity via cascade reactions of 2-amino-3 iodochromones with amines and carbon disulfide.RSC Adv. 2024 Jan 19;14(5):3158-3162. doi: 10.1039/d3ra07209f. eCollection 2024 Jan 17. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38249667 Free PMC article.
-
Multicomponent synthesis of chromophores - The one-pot approach to functional π-systems.Front Chem. 2023 Mar 17;11:1124209. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1124209. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 37007054 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

