On the Temporal Stability of Analyte Recognition with an E-Nose Based on a Metal Oxide Sensor Array in Practical Applications
- PMID: 29439468
- PMCID: PMC5856101
- DOI: 10.3390/s18020550
On the Temporal Stability of Analyte Recognition with an E-Nose Based on a Metal Oxide Sensor Array in Practical Applications
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Kiselev, I., et al. On the Temporal Stability of Analyte Recognition with an E-Nose Based on a Metal Oxide Sensor Array in Practical Applications. Sensors 2018, 18, 550.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Aug 12;19(16):3525. doi: 10.3390/s19163525. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31409006 Free PMC article.
Abstract
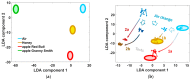
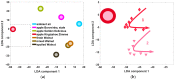
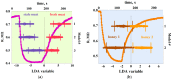
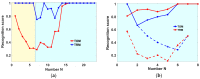
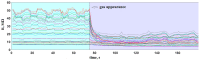
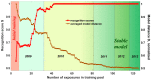
The paper deals with a functional instability of electronic nose (e-nose) units which significantly limits their real-life applications. Here we demonstrate how to approach this issue with example of an e-nose based on a metal oxide sensor array developed at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (Germany). We consider the instability of e-nose operation at different time scales ranging from minutes to many years. To test the e-nose we employ open-air and headspace sampling of analyte odors. The multivariate recognition algorithm to process the multisensor array signals is based on the linear discriminant analysis method. Accounting for the received results, we argue that the stability of device operation is mostly affected by accidental changes in the ambient air composition. To overcome instabilities, we introduce the add-training procedure which is found to successfully manage both the temporal changes of ambient and the drift of multisensor array properties, even long-term. The method can be easily implemented in practical applications of e-noses and improve prospects for device marketing.
Keywords: ambient air; electronic nose; honey recognition; instability; linear discriminant analysis; long-term stability; meat quality control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures






References
-
- Gardner J.W., Bartlett P.N. A brief history of electronic noses. Sens. Actuators B. 1993;18:211–220. doi: 10.1016/0925-4005(94)87085-3. - DOI
-
- Yang S., Jiang C., Wei S. Gas sensing in 2D materials. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2017;4:021304. doi: 10.1063/1.4983310. - DOI
-
- Morrison S.R. Selectivity in semiconductor gas sensors. Sens. Actuators. 1987;12:425–440. doi: 10.1016/0250-6874(87)80061-6. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

