Pharmacodynamics of Voriconazole for Invasive Pulmonary Scedosporiosis
- PMID: 29439967
- PMCID: PMC5923149
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02516-17
Pharmacodynamics of Voriconazole for Invasive Pulmonary Scedosporiosis
Abstract
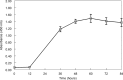
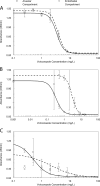
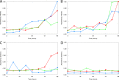
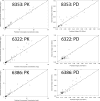
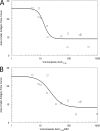
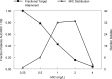
Scedosporium apiospermum is a medically important fungal pathogen that causes a wide range of infections in humans. There are relatively few antifungal agents that are active against Scedosporium spp. Little is known about the pharmacodynamics of voriconazole against Scedosporium Both static and dynamic in vitro models of invasive scedosporiosis were developed. Monoclonal antibodies that target a soluble cell wall antigen secreted by Scedosporium apiospermum were used to describe the pharmacodynamics of voriconazole. Mathematical pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic models were fitted to the data to estimate the drug exposure required to suppress the release of fungal antigen. The experimental results were bridged to humans using Monte Carlo simulation. All 3 strains of S. apiospermum tested invaded through the cellular bilayer of the in vitro models and liberated antigen. There was a concentration-dependent decline in the amount of antigen, with near maximal antifungal activity against all 3 strains being achieved with voriconazole at 10 mg/liter. Similarly, there was a drug exposure-dependent decline in the amount of circulating antigen in the dynamic model and complete suppression of antigen, with an area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) of approximately 80 mg · h/liter. A regression of the AUC/MIC versus the area under the antigen-time curve showed that a near maximal effect was obtained with an AUC/MIC of approximately 100. Monte Carlo simulation suggested that only isolates with an MIC of 0.5 mg/liter enabled pharmacodynamic targets to be achieved with a standard regimen of voriconazole. Isolates with higher MICs may need drug exposure targets higher than those currently recommended for other fungi.
Keywords: Scedosporium apiospermum; antifungal therapy; pharmacodynamics; pharmacokinetics; pneumonia; voriconazole.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
-
- Cortez KJ, Roilides E, Quiroz-Telles F, Meletiadis J, Antachopoulos C, Knudsen T, Buchanan W, Milanovich J, Sutton DA, Fothergill A, Rinaldi MG, Shea YR, Zaoutis T, Kottilil S, Walsh TJ. 2008. Infections caused by Scedosporium spp. Clin Microbiol Rev 21:157–197. doi:10.1128/CMR.00039-07. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gilgado F, Cano J, Gené J, Sutton DA, Guarro J. 2008. Molecular and phenotypic data supporting distinct species statuses for Scedosporium apiospermum and Pseudallescheria boydii and the proposed new species Scedosporium dehoogii. J Clin Microbiol 46:766–771. doi:10.1128/JCM.01122-07. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Husain S, Munoz P, Forrest G, Alexander BD, Somani J, Brennan K, Wagener MM, Singh N. 2005. Infections due to Scedosporium apiospermum and Scedosporium prolificans in transplant recipients: clinical characteristics and impact of antifungal agent therapy on outcome. Clin Infect Dis 40:89–99. doi:10.1086/426445. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

