Defusing inflammasomes
- PMID: 29440361
- PMCID: PMC5839772
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20180241
Defusing inflammasomes
Abstract
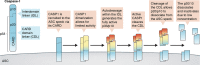
In this issue of JEM, Boucher et al. (https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20172222) report isolation of active caspase-1 from macrophages after inflammasome activation. Surprisingly, they find that caspase-1 is quickly inactivated upon autoproteolytic processing.
© 2018 Sandstrom and Vance.
Figures

Comment on
-
Caspase-1 self-cleavage is an intrinsic mechanism to terminate inflammasome activity.J Exp Med. 2018 Mar 5;215(3):827-840. doi: 10.1084/jem.20172222. Epub 2018 Feb 6. J Exp Med. 2018. PMID: 29432122 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

