Contribution of NIH funding to new drug approvals 2010-2016
- PMID: 29440428
- PMCID: PMC5878010
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1715368115
Contribution of NIH funding to new drug approvals 2010-2016
Abstract
This work examines the contribution of NIH funding to published research associated with 210 new molecular entities (NMEs) approved by the Food and Drug Administration from 2010-2016. We identified >2 million publications in PubMed related to the 210 NMEs (n = 131,092) or their 151 known biological targets (n = 1,966,281). Of these, >600,000 (29%) were associated with NIH-funded projects in RePORTER. This funding included >200,000 fiscal years of NIH project support (1985-2016) and project costs >$100 billion (2000-2016), representing ∼20% of the NIH budget over this period. NIH funding contributed to every one of the NMEs approved from 2010-2016 and was focused primarily on the drug targets rather than on the NMEs themselves. There were 84 first-in-class products approved in this interval, associated with >$64 billion of NIH-funded projects. The percentage of fiscal years of project funding identified through target searches, but not drug searches, was greater for NMEs discovered through targeted screening than through phenotypic methods (95% versus 82%). For targeted NMEs, funding related to targets preceded funding related to the NMEs, consistent with the expectation that basic research provides validated targets for targeted screening. This analysis, which captures basic research on biological targets as well as applied research on NMEs, suggests that the NIH contribution to research associated with new drug approvals is greater than previously appreciated and highlights the risk of reducing federal funding for basic biomedical research.
Keywords: NIH funding; basic science; drug development; translational science.
Copyright © 2018 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
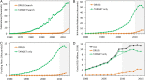
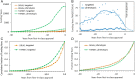
Comment in
-
NIH funding for research underlying new cancer therapies.Lancet Oncol. 2020 Jun;21(6):755-757. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30235-7. Lancet Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32502441 No abstract available.
References
-
- Stokes DE. Pasteur’s Quadrant: Basic Science and Technological Innovation. Brookings Institute; Washington, DC: 2011.
-
- Moses H, 3rd, et al. The anatomy of medical research: US and international comparisons. JAMA. 2015;313:174–189. - PubMed
-
- Zycher B, DiMasi JA, Milne C-P. Private sector contributions to pharmaceutical science: Thirty-five summary case histories. Am J Ther. 2010;17:101–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

