Generic assembly patterns in complex ecological communities
- PMID: 29440487
- PMCID: PMC5834670
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1710352115
Generic assembly patterns in complex ecological communities
Abstract
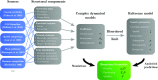
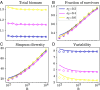
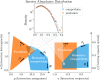
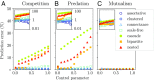
The study of ecological communities often involves detailed simulations of complex networks. However, our empirical knowledge of these networks is typically incomplete and the space of simulation models and parameters is vast, leaving room for uncertainty in theoretical predictions. Here we show that a large fraction of this space of possibilities exhibits generic behaviors that are robust to modeling choices. We consider a wide array of model features, including interaction types and community structures, known to generate different dynamics for a few species. We combine these features in large simulated communities, and show that equilibrium diversity, functioning, and stability can be predicted analytically using a random model parameterized by a few statistical properties of the community. We give an ecological interpretation of this "disordered" limit where structure fails to emerge from complexity. We also demonstrate that some well-studied interaction patterns remain relevant in large ecosystems, but their impact can be encapsulated in a minimal number of additional parameters. Our approach provides a powerful framework for predicting the outcomes of ecosystem assembly and quantifying the added value of more detailed models and measurements.
Keywords: community assembly; disordered systems; theoretical ecology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Loreau M. From Populations to Ecosystems: Theoretical Foundations for a New Ecological Synthesis (MPB-46) Princeton Univ Press; Princeton: 2010.
-
- Holt RD. Community modules in multitrophic interactions in terrestrial ecosystems, 36th Symposium of the British Ecological Society. Blackwell Sci; Oxford: 1997. pp. 333–349.
-
- Levins R. Discussion paper: The qualitative analysis of partially specified systems. Ann New York Acad Sci. 1974;231:123–138. - PubMed
-
- Brose U, Williams RJ, Martinez ND. Allometric scaling enhances stability in complex food webs. Ecol Lett. 2006;9:1228–1236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

