Cutting Edge: Check Your Mice-A Point Mutation in the Ncr1 Locus Identified in CD45.1 Congenic Mice with Consequences in Mouse Susceptibility to Infection
- PMID: 29440507
- PMCID: PMC5840015
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701676
Cutting Edge: Check Your Mice-A Point Mutation in the Ncr1 Locus Identified in CD45.1 Congenic Mice with Consequences in Mouse Susceptibility to Infection
Abstract
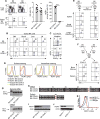
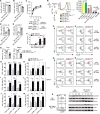
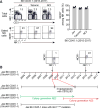
B6.SJL-Ptprca Pepcb /Boy (CD45.1) mice have been used in hundreds of congenic competitive transplants, with the presumption that they differ from C57BL/6 mice only at the CD45 locus. In this study, we describe a point mutation in the natural cytotoxicity receptor 1 (Ncr1) locus fortuitously identified in the CD45.1 strain. This point mutation was mapped at the 40th nucleotide of the Ncr1 locus causing a single amino acid mutation from cysteine to arginine at position 14 from the start codon, resulting in loss of NCR1 expression. We found that these mice were more resistant to CMV due to a hyper innate IFN-γ response in the absence of NCR1. In contrast, loss of NCR1 increased susceptibility to influenza virus, a result that is consistent with the role of NCR1 in the recognition of influenza Ag, hemagglutinin. This work sheds light on potential confounding experimental interpretation when this congenic strain is used as a tool for tracking lymphocyte development.
Copyright © 2018 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Single Targeted Exon Mutation Creates a True Congenic Mouse for Competitive Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: The C57BL/6-CD45.1(STEM) Mouse.Stem Cell Reports. 2016 Jun 14;6(6):985-992. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.04.010. Epub 2016 May 12. Stem Cell Reports. 2016. PMID: 27185283 Free PMC article.
-
Increased NK cell immunity in a transgenic mouse model of NKp46 overexpression.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 12;7(1):13090. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12998-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29026144 Free PMC article.
-
Conditional ablation of NKp46+ cells using a novel Ncr1(greenCre) mouse strain: NK cells are essential for protection against pulmonary B16 metastases.Eur J Immunol. 2014 Nov;44(11):3380-91. doi: 10.1002/eji.201444643. Epub 2014 Sep 19. Eur J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25142413
-
Expression, Function, and Molecular Properties of the Killer Receptor Ncr1-Noé.J Immunol. 2015 Oct 15;195(8):3959-69. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501234. Epub 2015 Sep 14. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26371250
-
Lessons from NK Cell Deficiencies in the Mouse.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2016;395:173-90. doi: 10.1007/82_2015_473. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26385768 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory T cells suppress the formation of potent KLRK1 and IL-7R expressing effector CD8 T cells by limiting IL-2.Elife. 2023 Jan 27;12:e79342. doi: 10.7554/eLife.79342. Elife. 2023. PMID: 36705564 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Killer Cell Recruitment to the Lung During Influenza A Virus Infection Is Dependent on CXCR3, CCR5, and Virus Exposure Dose.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 17;9:781. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00781. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29719539 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of a C57BL/6J mouse strain expressing the CD45.1 epitope to improve hematopoietic stem cell engraftment and adoptive cell transfer experiments.Lab Anim (NY). 2023 Dec;52(12):324-331. doi: 10.1038/s41684-023-01275-1. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Lab Anim (NY). 2023. PMID: 38017180
-
The Applicability of Mouse Models to the Study of Human Disease.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1940:3-22. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9086-3_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30788814 Free PMC article.
-
A membrane lipid signature unravels the dynamic landscape of group 1 innate lymphoid cells across the health-disease continuum.iScience. 2025 Feb 17;28(3):112043. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112043. eCollection 2025 Mar 21. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40104068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ryan MA, Nattamai KJ, Xing E, Schleimer D, Daria D, Sengupta A, Kohler A, Liu W, Gunzer M, Jansen M, Ratner N, Le Cras TD, Waterstrat A, Van Zant G, Cancelas JA, Zheng Y, Geiger H. Pharmacological inhibition of EGFR signaling enhances G-CSF-induced hematopoietic stem cell mobilization. Nat Med. 2010;16:1141–1146. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Morgan XC, Kabakchiev B, Waldron L, Tyler AD, Tickle TL, Milgrom R, Stempak JM, Gevers D, Xavier RJ, Silverberg MS, Huttenhower C. Associations between host gene expression, the mucosal microbiome, and clinical outcome in the pelvic pouch of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Genome biology. 2015;16:67. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Martoglio B, Dobberstein B. Signal sequences: more than just greasy peptides. Trends Cell Biol. 1998;8:410–415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

