Control of Homeostatic Synaptic Plasticity by AKAP-Anchored Kinase and Phosphatase Regulation of Ca2+-Permeable AMPA Receptors
- PMID: 29440558
- PMCID: PMC5852664
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2362-17.2018
Control of Homeostatic Synaptic Plasticity by AKAP-Anchored Kinase and Phosphatase Regulation of Ca2+-Permeable AMPA Receptors
Abstract
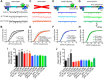
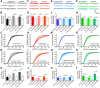
Neuronal information processing requires multiple forms of synaptic plasticity mediated by NMDARs and AMPA-type glutamate receptors (AMPARs). These plasticity mechanisms include long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD), which are Hebbian, homosynaptic mechanisms locally regulating synaptic strength of specific inputs, and homeostatic synaptic scaling, which is a heterosynaptic mechanism globally regulating synaptic strength across all inputs. In many cases, LTP and homeostatic scaling regulate AMPAR subunit composition to increase synaptic strength via incorporation of Ca2+-permeable receptors (CP-AMPAR) containing GluA1, but lacking GluA2, subunits. Previous work by our group and others demonstrated that anchoring of the kinase PKA and the phosphatase calcineurin (CaN) to A-kinase anchoring protein (AKAP) 150 play opposing roles in regulation of GluA1 Ser845 phosphorylation and CP-AMPAR synaptic incorporation during hippocampal LTP and LTD. Here, using both male and female knock-in mice that are deficient in PKA or CaN anchoring, we show that AKAP150-anchored PKA and CaN also play novel roles in controlling CP-AMPAR synaptic incorporation during homeostatic plasticity in hippocampal neurons. We found that genetic disruption of AKAP-PKA anchoring prevented increases in Ser845 phosphorylation and CP-AMPAR synaptic recruitment during rapid homeostatic synaptic scaling-up induced by combined blockade of action potential firing and NMDAR activity. In contrast, genetic disruption of AKAP-CaN anchoring resulted in basal increases in Ser845 phosphorylation and CP-AMPAR synaptic activity that blocked subsequent scaling-up by preventing additional CP-AMPAR recruitment. Thus, the balanced, opposing phospho-regulation provided by AKAP-anchored PKA and CaN is essential for control of both Hebbian and homeostatic plasticity mechanisms that require CP-AMPARs.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Neuronal circuit function is shaped by multiple forms of activity-dependent plasticity that control excitatory synaptic strength, including LTP/LTD that adjusts strength of individual synapses and homeostatic plasticity that adjusts overall strength of all synapses. Mechanisms controlling LTP/LTD and homeostatic plasticity were originally thought to be distinct; however, recent studies suggest that CP-AMPAR phosphorylation regulation is important during both LTP/LTD and homeostatic plasticity. Here we show that CP-AMPAR regulation by the kinase PKA and phosphatase CaN coanchored to the scaffold protein AKAP150, a mechanism previously implicated in LTP/LTD, is also crucial for controlling synaptic strength during homeostatic plasticity. These novel findings significantly expand our understanding of homeostatic plasticity mechanisms and further emphasize how intertwined they are with LTP and LTD.
Keywords: AKAP150; Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptor; LTP; PKA; calcineurin; homeostatic plasticity.
Copyright © 2018 the authors 0270-6474/18/382863-14$15.00/0.
Figures



Similar articles
-
β-Amyloid disruption of LTP/LTD balance is mediated by AKAP150-anchored PKA and Calcineurin regulation of Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors.Cell Rep. 2021 Oct 5;37(1):109786. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109786. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34610314 Free PMC article.
-
NMDA Receptor-Dependent LTD Requires Transient Synaptic Incorporation of Ca²⁺-Permeable AMPARs Mediated by AKAP150-Anchored PKA and Calcineurin.Neuron. 2016 Mar 2;89(5):1000-15. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.01.043. Neuron. 2016. PMID: 26938443 Free PMC article.
-
AKAP150-anchored calcineurin regulates synaptic plasticity by limiting synaptic incorporation of Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors.J Neurosci. 2012 Oct 24;32(43):15036-52. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3326-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23100425 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of neuronal PKA signaling through AKAP targeting dynamics.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;85(7):627-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.01.010. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16504338 Review.
-
The AMPA Receptor Code of Synaptic Plasticity.Neuron. 2018 Oct 24;100(2):314-329. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.10.018. Neuron. 2018. PMID: 30359599 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
AKAP150 Palmitoylation Regulates Synaptic Incorporation of Ca2+-Permeable AMPA Receptors to Control LTP.Cell Rep. 2018 Oct 23;25(4):974-987.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.09.085. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30355502 Free PMC article.
-
β-Amyloid disruption of LTP/LTD balance is mediated by AKAP150-anchored PKA and Calcineurin regulation of Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors.Cell Rep. 2021 Oct 5;37(1):109786. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109786. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34610314 Free PMC article.
-
Palmitoylation of A-kinase anchoring protein 79/150 modulates its nanoscale organization, trafficking, and mobility in postsynaptic spines.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2022 Sep 15;14:1004154. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2022.1004154. eCollection 2022. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36186623 Free PMC article.
-
Latrophilin GPCR signaling mediates synapse formation.Elife. 2021 Mar 1;10:e65717. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65717. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33646123 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Role of protein palmitoylation in synaptic plasticity and neuronal differentiation, volume II.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2024 Sep 10;16:1473989. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2024.1473989. eCollection 2024. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39319198 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
