Reconsideration of Amyloid Hypothesis and Tau Hypothesis in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 29440986
- PMCID: PMC5797629
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00025
Reconsideration of Amyloid Hypothesis and Tau Hypothesis in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
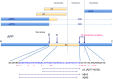
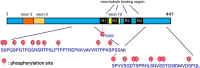
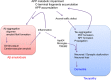
The so-called amyloid hypothesis, that the accumulation and deposition of oligomeric or fibrillar amyloid β (Aβ) peptide is the primary cause of Alzheimer's disease (AD), has been the mainstream concept underlying AD research for over 20 years. However, all attempts to develop Aβ-targeting drugs to treat AD have ended in failure. Here, we review recent findings indicating that the main factor underlying the development and progression of AD is tau, not Aβ, and we describe the deficiencies of the amyloid hypothesis that have supported the emergence of this idea.
Keywords: APP; Alzheimer's disease; Aβ; PHF; amyloid; tau.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

