Self-Shielding Analysis of the Zap-X System
- PMID: 29441251
- PMCID: PMC5800761
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1917
Self-Shielding Analysis of the Zap-X System
Erratum in
-
Correction: Self-Shielding Analysis of the Zap-X System.Cureus. 2019 May 17;11(5):c22. doi: 10.7759/cureus.c22. Cureus. 2019. PMID: 31149412 Free PMC article.
Abstract
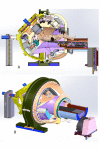
The Zap-X is a self-contained and first-of-its-kind self-shielded therapeutic radiation device dedicated to brain as well as head and neck stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). By utilizing an S-band linear accelerator (linac) with a 2.7 megavolt (MV) accelerating potential and incorporating radiation-shielded mechanical structures, the Zap-X does not typically require a radiation bunker, thereby saving SRS facilities considerable cost. At the same time, the self-shielded features of the Zap-X are designed for more consistency of radiation protection, reducing the risk to radiation workers and others potentially exposed from a poorly designed or constructed radiotherapy vault. The hypothesis of the present study is that a radiosurgical system can be self-shielded such that it produces radiation exposure levels deemed safe to the public while operating under a full clinical workload. This study summarizes the Zap-X system shielding and found that the overall system radiation leakage values are reduced by a factor of 50 compared to the occupational radiation limit stipulated by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) or agreement states. The goal of self-shielding is achieved under all but the most exceptional conditions for which additional room shielding or a larger restricted area in the vicinity of the Zap-X system would be required.
Keywords: radiation; radiation exposure; radiation shielding; self-shielded; stereotactic radiosurgery.
Conflict of interest statement
9,308,395 9,757,594 PCT/US2017/038256 PCT/US 2017/054880 29/616,477
Figures
References
-
- National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurement – NCRP reports (#49, 51, 116, 151) [Nov;2017 ];http://www.ncrppublications.org/reports 2014
-
- BEAM: a Monte Carlo code to simulate radiotherapy treatment units. [Nov;2017 ];Rogers DW, Faddegon BA, Ding GX, et al. Med Phys. 1995 22:503–524. - PubMed
-
- BEAMnrc user’s manual, NRC report PIRS 509(a), rev I, 2011. [Nov;2017 ];http://www.researchgate.net/profile/C-M_Charlie_Ma/publication/44076214_... 2014
-
- Siebers JV, Keall PJ, Kawrakow I. The Modern Technology of Radiation Oncology: A Compendium for Medical Physicists and Radiation Oncologists. Vol. 2. Madison, WI: Medical Physics Publishing; 2005. Monte Carlo dose calculation for external beam radiotherapy; p. 514.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources