Neurometabolic disorders: Five new things
- PMID: 29443118
- PMCID: PMC5727707
- DOI: 10.1212/CPJ.0000000000000266
Neurometabolic disorders: Five new things
Abstract
Purpose of review: To present emerging issues in neurometabolic disorders, with an emphasis on the diagnostic workup of patients with suspected neurometabolic disorders and some future challenges in the care for these patients.
Recent findings: Next-generation sequencing and next-generation metabolic screening increase the speed and yield of the diagnostic process in neurometabolic disorders. Furthermore, they deepen our insights into the underlying disease mechanisms. Care of adult patients with neurometabolic disorders is an expanding subspecialty, especially in internal medicine and neurology.
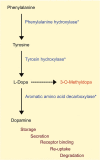
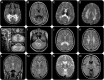
Summary: We briefly discuss some novel genetic and biochemical laboratory techniques and changing insights in the molecular basis of disease, and illustrate the importance of MRI pattern recognition in the diagnostic process. Furthermore, we discuss gene therapy that is cautiously entering the field, and pay attention to the new field of (transition of) care for adult patients with inborn errors of metabolism.
Figures
References
-
- Morava E, Rahman S, Peters V, Baumgartner MR, Patterson M, Zschocke J. Quo vadis: the re-definition of “inborn metabolic diseases.” J Inherit Metab Dis 2015;38:1003–1006. - PubMed
-
- Gilissen C, Hehir-Kwa JY, Thung DT, et al. . Genome sequencing identifies major causes of severe intellectual disability. Nature 2014;511:344–347. - PubMed
-
- Wortmann S, Rodenburg RJ, Huizing M, et al. . Association of 3-methylglutaconic aciduria with sensorineural deafness, encephalopathy, and Leigh-like syndrome (MEGDEL association) in four patients with a disorder of the oxidative phosphorylation. Mol Genet Metab 2006;88:47–52. - PubMed
-
- Wortmann SB, van Hasselt PM, Baric I, et al. . Eyes on MEGDEL: distinctive basal ganglia involvement in dystonia deafness syndrome. Neuropediatrics 2015;46:98–103. - PubMed
-
- Wortmann SB, Vaz FM, Gardeitchik T, et al. . Mutations in the phospholipid remodeling gene SERAC1 impair mitochondrial function and intracellular cholesterol trafficking and cause dystonia and deafness. Nat Genet 2012;44:797–802. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
