Changes in the Anti-Allergic Activities of Sesame by Bioconversion
- PMID: 29443928
- PMCID: PMC5852786
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10020210
Changes in the Anti-Allergic Activities of Sesame by Bioconversion
Abstract
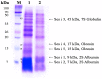
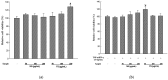
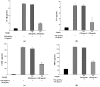
Sesame is an important oilseed crop, which has been used as a traditional health food to ameliorate the prevention of various diseases. We evaluated the changes in the anti-allergic activities of sesame by bioconversion. SDS-PAGE of non-fermented sesame proteins showed major allergen bands, while that of fermented sesame showed only a few protein bands. Additionally, we investigated the effectiveness of fermented sesame by bioconversion in tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)- and interferon-γ (IFN-γ)-induced HaCaT cells. In HaCaT cells, fermented sesame inhibited the mRNA expression of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β), thymus and macrophage-derived chemokine (MDC/CCL22), activation-regulated chemokine (TARC/CCL17), and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1). Moreover, fermented sesame inhibited the activation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1). Fermented sesame exerts anti-allergic effects by suppressing the expression of chemokines and cytokines via blockade of NF-κB and STAT1 activation.
Keywords: Sesamum indicum L.; anti-allergic; atopic dermatitis; bioconversion; skin inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Suja K.P., Jayalekshmy A., Arumughan C. Antioxidant activity of sesame cake extract. Food Chem. 2005;91:213–219. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2003.09.001. - DOI
-
- Kang M.H., Naito M., Tsujihara N., Osawa T. Sesamolin inhibits lipid peroxidation in rat liver and kidney. J. Nutr. 1998;128:1018–1022. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

