A real-time monitoring platform of myogenesis regulators using double fluorescent labeling
- PMID: 29444187
- PMCID: PMC5812636
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192654
A real-time monitoring platform of myogenesis regulators using double fluorescent labeling
Abstract
Real-time, quantitative measurement of muscle progenitor cell (myoblast) differentiation is an important tool for skeletal muscle research and identification of drugs that support skeletal muscle regeneration. While most quantitative tools rely on sacrificial approach, we developed a double fluorescent tagging approach, which allows for dynamic monitoring of myoblast differentiation through assessment of fusion index and nuclei count. Fluorescent tagging of both the cell cytoplasm and nucleus enables monitoring of cell fusion and the formation of new myotube fibers, similar to immunostaining results. This labeling approach allowed monitoring the effects of Myf5 overexpression, TNFα, and Wnt agonist on myoblast differentiation. It also enabled testing the effects of surface coating on the fusion levels of scaffold-seeded myoblasts. The double fluorescent labeling of myoblasts is a promising technique to visualize even minor changes in myogenesis of myoblasts in order to support applications such as tissue engineering and drug screening.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
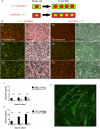
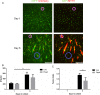


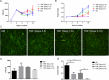

References
-
- Houle D, Govindaraju DR, Omholt S (2010) Phenomics: the next challenge. Nature reviews genetics 11: 855–866. doi: 10.1038/nrg2897 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cornelison D, Perdiguero E (2017) Muscle Stem Cells: A Model System for Adult Stem Cell Biology. Muscle Stem Cells: Methods and Protocols: 3–19. - PubMed
-
- Charge SB, Rudnicki MA (2004) Cellular and molecular regulation of muscle regeneration. Physiological reviews 84: 209–238. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00019.2003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wagers AJ, Conboy IM (2005) Cellular and molecular signatures of muscle regeneration: current concepts and controversies in adult myogenesis. Cell 122: 659–667. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.021 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Millay DP, O’Rourke JR, Sutherland LB, Bezprozvannaya S, Shelton JM, et al. (2013) Myomaker is a membrane activator of myoblast fusion and muscle formation. Nature 499: 301–305. doi: 10.1038/nature12343 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

