Endovascular treatment of cerebral aneurysm after renal transplantation in polycystic kidney disease
- PMID: 29444616
- PMCID: PMC5967191
- DOI: 10.1177/1591019918758037
Endovascular treatment of cerebral aneurysm after renal transplantation in polycystic kidney disease
Abstract
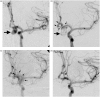
Background Patients with polycystic kidney disease have a higher prevalence of intracranial aneurysms and may progress to renal failure requiring transplantation. The endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms may improve prognosis, since rupture often causes premature death or disability, but the nephrotoxicity risk associated with contrast medium must be always considered in cases of renal impairment. Methods A 55-year-old female patient with polycystic kidney disease and grafted kidney associated with anterior communicant artery aneurysm was successfully treated by embolization. Results The renal function remained normal after the procedure. To the authors' knowledge, this is the first case of endovascular treatment of brain aneurysm in a transplanted patient reported in the medical literature. Conclusions The endovascular procedure in renal transplant patients is feasible and can be considered to treat this population. Further studies and cases are needed to confirm its safety.
Keywords: Kidney transplantation; endovascular procedures; intracranial aneurysm; polycystic kidney disease.
Figures

References
-
- Cagnazzo F, Gambacciani C, Morganti R, et al. Intracranial aneurysms in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: Prevalence, risk of rupture, and management. A systematic review. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2017; 159: 811–821. - PubMed
-
- Schievink WI, Torres VE, Piepgras DG, et al. Saccular intracranial aneurysms in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 1992; 3: 88–95. - PubMed
-
- Chapman AB, Rubinstein D, Hughes R, et al. Intracranial aneurysms in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 1992; 327: 916–920. - PubMed
-
- Huston J, 3rd, Torres VE, Sulivan PP, et al. Value of magnetic resonance angiography for the detection of intracranial aneurysms in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 1993; 3: 1871–1877. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

