Effect of tt-farnesol and myricetin on in vitro biofilm formed by Streptococcus mutans and Candida albicans
- PMID: 29444673
- PMCID: PMC5813409
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-018-2132-x
Effect of tt-farnesol and myricetin on in vitro biofilm formed by Streptococcus mutans and Candida albicans
Abstract
Background: Dental caries is considered a multifactorial disease, in which microorganisms play an important role. The diet is decisive in the biofilm formation because it provides the necessary resources for cellular growth and exopolysaccharides synthesis. Exopolysaccharides are the main components of the extracellular matrix (ECM). The ECM provides a 3D structure, support for the microorganisms and form diffusion-limited environments (acidic niches) that cause demineralization of the dental enamel. Streptococcus mutans is the main producer of exopolysaccharides. Candida albicans is detected together with S. mutans in biofilms associated with severe caries lesions. Thus, this study aimed to determine the effect of tt-farnesol and myricetin topical treatments on cariogenic biofilms formed by Streptococcus mutans and Candida albicans.
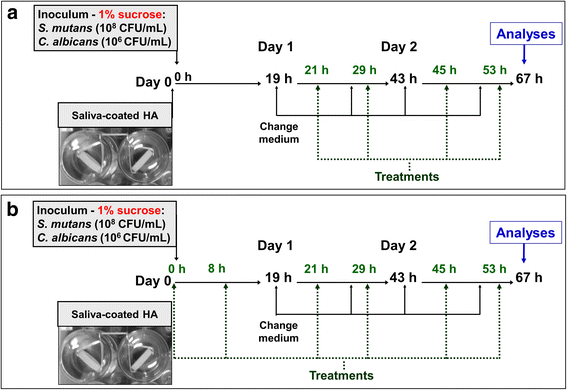
Methods: In vitro dual-species biofilms were grown on saliva-coated hydroxyapatite discs, using tryptone-yeast extract broth with 1% sucrose (37 °C, 5% CO2). Twice-daily topical treatments were performed with: vehicle (ethanol 15%, negative control), 2 mM myricetin, 4 mM tt-farnesol, myricetin + tt-farnesol, myricetin + tt-farnesol + fluoride (250 ppm), fluoride, and chlorhexidine digluconate (0.12%; positive control). After 67 h, biofilms were evaluated to determine biofilm biomass, microbial population, and water-soluble and -insoluble exopolysaccharides in the ECM.
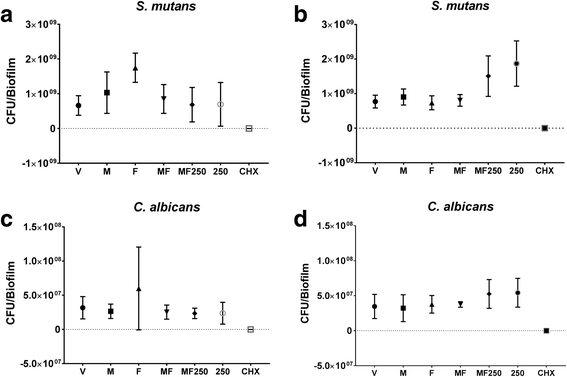
Results: Only the positive control yielded a reduced quantity of biomass and microbial population, while tt-farnesol treatment was the least efficient in reducing C. albicans population. The combination therapy myricetin + farnesol + fluoride significantly reduced water-soluble exopolysaccharides in the ECM (vs. negative control; p < 0.05; ANOVA one-way, followed by Tukey's test), similarly to the positive control.
Conclusions: Therefore, the combination therapy negatively influenced an important virulence trait of cariogenic biofilms. However, the concentrations of both myricetin and tt-farnesol should be increased to produce a more pronounced effect to control these biofilms.
Keywords: Candida albicans; Cariogenic biofilm; Myricetin; Streptococcus Mutans; Topical treatment; tt-farnesol.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All volunteers received an explanation about the study and consented to donated saliva for pellicle formation by signing an informed consent term. The study was approved by the Institutional Ethical Committee at São Paulo State University (Unesp), School of Dentistry, Araraquara. (CAAE: 31.725.114.8.0000.5416).
Consent for publication
“Not applicable”. Saliva samples were pooled without volunteer identification.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



References
-
- Bagramian RA, Garcia-Godoy F, Volpe AR. The global increase in dental caries. A pending public health crisis. Am J Dent. 2009;21:3–8. - PubMed
-
- Kidd EA, Fejerskov O. What constitutes dental caries? Histopathology of carious enamel and dentin related to the action of cariogenic biofilms. J Dent Res. 2004;83 Spec No C:C35–C38. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

