Multiple Applications of a Transient CRISPR-Cas9 Coupled with Electroporation (TRACE) System in the Cryptococcus neoformans Species Complex
- PMID: 29444806
- PMCID: PMC5887135
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.117.300656
Multiple Applications of a Transient CRISPR-Cas9 Coupled with Electroporation (TRACE) System in the Cryptococcus neoformans Species Complex
Abstract
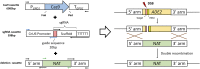
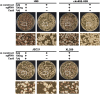
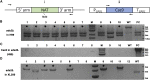
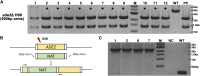
Cryptococcus neoformans is a fungal pathogen that claims hundreds of thousands of lives annually. Targeted genetic manipulation through biolistic transformation in C. neoformans drove the investigation of this clinically important pathogen at the molecular level. Although costly and inefficient, biolistic transformation remains the major method for editing the Cryptococcus genome as foreign DNAs introduced by other methods such as electroporation are predominantly not integrated into the genome. Although the majority of DNAs introduced by biolistic transformation are stably inherited, the transformation efficiency and the homologous integration rate (∼1-10%) are low. Here, we developed a
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas9; Cryptococcus neoformans; biolistic transformation; double-strand break; ectopic integration; electroporation; gene complementation; gene disruption; gene family.
Copyright © 2018 by the Genetics Society of America.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

