Dusp6 attenuates Ras/MAPK signaling to limit zebrafish heart regeneration
- PMID: 29444893
- PMCID: PMC5868992
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.157206
Dusp6 attenuates Ras/MAPK signaling to limit zebrafish heart regeneration
Abstract
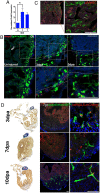
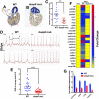
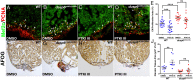
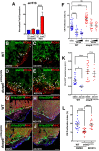
Zebrafish regenerate cardiac tissue through proliferation of pre-existing cardiomyocytes and neovascularization. Secreted growth factors such as FGFs, IGF, PDGFs and Neuregulin play essential roles in stimulating cardiomyocyte proliferation. These factors activate the Ras/MAPK pathway, which is tightly controlled by the feedback attenuator Dual specificity phosphatase 6 (Dusp6), an ERK phosphatase. Here, we show that suppressing Dusp6 function enhances cardiac regeneration. Inactivation of Dusp6 by small molecules or by gene inactivation increased cardiomyocyte proliferation, coronary angiogenesis, and reduced fibrosis after ventricular resection. Inhibition of Erbb or PDGF receptor signaling suppressed cardiac regeneration in wild-type zebrafish, but had a milder effect on regeneration in dusp6 mutants. Moreover, in rat primary cardiomyocytes, NRG1-stimulated proliferation can be enhanced upon chemical inhibition of Dusp6 with BCI. Our results suggest that Dusp6 attenuates Ras/MAPK signaling during regeneration and that suppressing Dusp6 can enhance cardiac repair.
Keywords: Cardiac repair; Cardiomyocyte proliferation; Dual specificity phosphatase 6; Heart regeneration; Ras/MAPK signaling; Zebrafish.
© 2018. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The FGF-AKT pathway is necessary for cardiomyocyte survival for heart regeneration in zebrafish.Dev Biol. 2021 Apr;472:30-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2020.12.019. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33444612 Free PMC article.
-
A parental requirement for dual-specificity phosphatase 6 in zebrafish.BMC Dev Biol. 2018 Mar 15;18(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12861-018-0164-6. BMC Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29544468 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of dual-specificity phosphatase 6, a negative regulator of oncogenic ERK signaling, by ACA-28 induces apoptosis in NIH/3T3 cells overexpressing HER2/ErbB2.Genes Cells. 2021 Feb;26(2):109-116. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12823. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Genes Cells. 2021. PMID: 33249692
-
How can the adult zebrafish and neonatal mice teach us about stimulating cardiac regeneration in the human heart?Regen Med. 2023 Jan;18(1):85-99. doi: 10.2217/rme-2022-0161. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Regen Med. 2023. PMID: 36416596 Review.
-
Zebrafish heart regeneration: Factors that stimulate cardiomyocyte proliferation.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Apr;100:3-10. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2019.09.005. Epub 2019 Sep 25. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 31563389 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Gridlock transcriptional repressor impedes vertebrate heart regeneration by restricting expression of lysine methyltransferase.Development. 2020 Sep 28;147(18):dev190678. doi: 10.1242/dev.190678. Development. 2020. PMID: 32988975 Free PMC article.
-
DUSP6 Inhibitor (E/Z)-BCI Hydrochloride Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses in Murine Macrophage Cells via Activating the Nrf2 Signaling Axis and Inhibiting the NF-κB Pathway.Inflammation. 2019 Apr;42(2):672-681. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0924-2. Inflammation. 2019. PMID: 30506106
-
Enhancing regeneration after acute kidney injury by promoting cellular dedifferentiation in zebrafish.Dis Model Mech. 2019 Apr 5;12(4):dmm037390. doi: 10.1242/dmm.037390. Dis Model Mech. 2019. PMID: 30890583 Free PMC article.
-
N-Acetyltransferase 10 represses Uqcr11 and Uqcrb independently of ac4C modification to promote heart regeneration.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 8;15(1):2137. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46458-7. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38459019 Free PMC article.
-
Dual specificity phosphatase 7 drives the formation of cardiac mesoderm in mouse embryonic stem cells.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 13;17(10):e0275860. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0275860. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36227898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cade L., Reyon D., Hwang W. Y., Tsai S. Q., Patel S., Khayter C., Joung J. K., Sander J. D., Peterson R. T. and Yeh J.-R. J. (2012). Highly efficient generation of heritable zebrafish gene mutations using homo- and heterodimeric TALENs. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, 8001-8010. 10.1093/nar/gks518 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

