Kinesin 1 regulates cilia length through an interaction with the Bardet-Biedl syndrome related protein CCDC28B
- PMID: 29445114
- PMCID: PMC5813027
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-21329-6
Kinesin 1 regulates cilia length through an interaction with the Bardet-Biedl syndrome related protein CCDC28B
Abstract
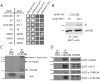
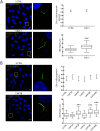
Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS) is a ciliopathy characterized by retinal degeneration, obesity, polydactyly, renal disease and mental retardation. CCDC28B is a BBS-associated protein that we have previously shown plays a role in cilia length regulation whereby its depletion results in shortened cilia both in cells and Danio rerio (zebrafish). At least part of that role is achieved by its interaction with the mTORC2 component SIN1, but the mechanistic details of this interaction and/or additional functions that CCDC28B might play in the context of cilia remain poorly understood. Here we uncover a novel interaction between CCDC28B and the kinesin 1 molecular motor that is relevant to cilia. CCDC28B interacts with kinesin light chain 1 (KLC1) and the heavy chain KIF5B. Notably, depletion of these kinesin 1 components results in abnormally elongated cilia. Furthermore, through genetic interaction studies we demonstrate that kinesin 1 regulates ciliogenesis through CCDC28B. We show that kinesin 1 regulates the subcellular distribution of CCDC28B, unexpectedly, inhibiting its nuclear accumulation, and a ccdc28b mutant missing a nuclear localization motif fails to rescue the phenotype in zebrafish morphant embryos. Therefore, we uncover a previously unknown role of kinesin 1 in cilia length regulation that relies on the BBS related protein CCDC28B.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Generation and characterization of Ccdc28b mutant mice links the Bardet-Biedl associated gene with mild social behavioral phenotypes.PLoS Genet. 2022 Jun 2;18(6):e1009896. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009896. eCollection 2022 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 35653384 Free PMC article.
-
The Bardet-Biedl syndrome-related protein CCDC28B modulates mTORC2 function and interacts with SIN1 to control cilia length independently of the mTOR complex.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Oct 15;22(20):4031-42. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt253. Epub 2013 May 31. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23727834 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of CCDC28B reveals its role in ciliogenesis and provides insight to understand its modifier effect on Bardet-Biedl syndrome.Hum Genet. 2013 Jan;132(1):91-105. doi: 10.1007/s00439-012-1228-5. Epub 2012 Sep 27. Hum Genet. 2013. PMID: 23015189
-
Establishing a connection between cilia and Bardet-Biedl Syndrome.Trends Mol Med. 2004 Mar;10(3):106-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2004.01.003. Trends Mol Med. 2004. PMID: 15106604 Review.
-
Retinal Degeneration Animal Models in Bardet-Biedl Syndrome and Related Ciliopathies.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2023 Jan 3;13(1):a041303. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a041303. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2023. PMID: 36596648 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Generation and characterization of Ccdc28b mutant mice links the Bardet-Biedl associated gene with mild social behavioral phenotypes.PLoS Genet. 2022 Jun 2;18(6):e1009896. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009896. eCollection 2022 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 35653384 Free PMC article.
-
Dominant negative variants in KIF5B cause osteogenesis imperfecta via down regulation of mTOR signaling.PLoS Genet. 2023 Nov 7;19(11):e1011005. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011005. eCollection 2023 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 37934770 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Deacetylation Enzymes Hdac6 and Sirt2 Promotes Acetylation of Cytoplasmic Tubulin, but Suppresses Axonemal Acetylation in Zebrafish Cilia.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 28;9:676214. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.676214. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34268305 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Both Associated with Hypertension and Contributing to Accelerated-Senescence Traits in OXYS Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 17;21(10):3542. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103542. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32429546 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome-wide association identifies KLC1 as a regulator of mitophagy in non-syndromic cleft lip with or without palate.Imeta. 2024 Dec 20;3(6):e262. doi: 10.1002/imt2.262. eCollection 2024 Dec. Imeta. 2024. PMID: 39742305 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

