Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with zonisamide
- PMID: 29445458
- PMCID: PMC5799627
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.1288
Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with zonisamide
Abstract
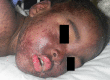
This report highlights zonisamide as a potential cause of serious cutaneous reactions as well as its cross-reactivity with other sulfonamides. Here, we present a case of SJS-TEN due to zonisamide, which was effectively treated with IVIg. Subsequently, the patient was transitioned to levetiracetam for seizure control.
Keywords: Drug rash; Stevens–Johnson syndrome; pediatric; toxic epidermal necrolysis; zonisamide.
Figures


References
-
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research . Zonegran NDA 20‐789 approval letter, March 27, 2000. Available at https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2000/020789_Zonegran_... (accessed 9 May 2017).
-
- Biton, V. 2007. Clinical pharmacology and mechanism of action of zonisamide. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 30:230–240. - PubMed
-
- Baulac, M. , Brodie M. J., Patten A., Segieth J., and Giorgi L.. 2012. Efficacy and tolerability of zonisamide versus controlled‐release carbamazepine for newly diagnosed partial epilepsy: a phase 3, randomized, double‐blind, non‐inferiority trial. Lancet Neurol. 11:579–588. - PubMed
-
- Buoli, M. , Grassi S., Ciappolino V., Serati M., and Altamura A. C.. 2017. The use of zonisamide for the treatment of psychiatric disorders: a systematic review. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 40:85–92. - PubMed
-
- Baulac, M. , Patten A., and Giorgi L.. 2014. Long‐term safety and efficacy of zonisamide versus carbamazepine monotherapy for treatment of partial seizures in adults with newly diagnosed epilepsy: results of a phase III, randomized, double‐blind study. Epilepsia 55:1534–1543. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

