Model-Informed Drug Development for Ixazomib, an Oral Proteasome Inhibitor
- PMID: 29446068
- PMCID: PMC6585617
- DOI: 10.1002/cpt.1047
Model-Informed Drug Development for Ixazomib, an Oral Proteasome Inhibitor
Abstract
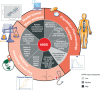
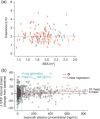
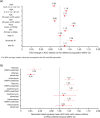
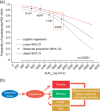
Model-informed drug development (MIDD) was central to the development of the oral proteasome inhibitor ixazomib, facilitating internal decisions (switch from body surface area (BSA)-based to fixed dosing, inclusive phase III trials, portfolio prioritization of ixazomib-based combinations, phase III dose for maintenance treatment), regulatory review (model-informed QT analysis, benefit-risk of 4 mg dose), and product labeling (absolute bioavailability and intrinsic/extrinsic factors). This review discusses the impact of MIDD in enabling patient-centric therapeutic optimization during the development of ixazomib.
© 2017 The Authors. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
N.G., M.J.H., H.Y., Z.T., R.L., D.B., C.P., G.L., H.vdV., and K.V. are employees of Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Cambridge, MA, USA, a wholly owned subsidiary of Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited. P.M.D. is an employee of Certara Strategic Consulting, Breda, The Netherlands, which conducted analytical work for Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. A.K. is an employee of Certara USA, Inc., Princeton, NJ, USA, which conducted analytical work for Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. As an Associate Editor for
Figures


References
-
- Millennium Pharmaceuticals Inc . NINLARO® (ixazomib) capsules, for oral use. United States Prescribing Information. 2016.
-
- Takeda Pharma A/S . NINLARO: European Product Assessment Report (EPAR) — Product Information. Annex I — Summary of Product Characteristics. 2017.
-
- Moreau, P. et al Oral ixazomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone for multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 374, 1621–1634 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

