The impact of EGFR mutations on the incidence and survival of stages I to III NSCLC patients with subsequent brain metastasis
- PMID: 29447182
- PMCID: PMC5813924
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192161
The impact of EGFR mutations on the incidence and survival of stages I to III NSCLC patients with subsequent brain metastasis
Abstract
Previous studies have demonstrated the association between EGFR mutations and distant metastasis. However, the association for subsequent brain metastasis (BM) in stages I-III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients remains inconclusive. We conducted a retrospective analysis to clarify the impact of EGFR mutations on the incidence of BM and associated survival in patients with stage I-III NSCLC. A total of 491 patients screened for EGFR mutations were retrospectively enrolled. Brain MRI or CT was used to detect the BM. Cumulative incidence of subsequent BM and overall survival (OS) after diagnosis of BM were estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method and compared using log-rank test. We performed Cox proportional hazard regression for predictors of subsequent BM and determinants of OS after BM. The cumulative incidence of BM seemed higher in patients harboring EGFR mutations than those without EGFR mutations although it did not reach statistical significance (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.75, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.73~1.81). After adjusting possible confounders, including age, smoking, stage, and tumor size, EGFR mutation became one of the predictors for subsequent BM (HR = 1.89, 95% CI = 1.12~3.17, p = 0.017). Though there was no statistical difference in survival after BM between patients with EGFR mutations and wild-type EGFR (median survival: 17.8 vs. 12.2 months, HR = 0.79, 95% CI = 0.45-1.40), patients with EGFR 19 deletion (Del) tended to have a longer survival after BM than the non-EGFR 19 Del group (median survival: 29.4 vs. 14.3 months, HR 0.58, 95% CI = 0.32-1.09, p = 0.089). In conclusion, our data suggested EGFR mutation to be one of the predictors for subsequent BM in stage I-III patients. Given the small sample size, more studies are warranted to corroborate our results.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

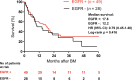
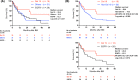
References
-
- Venur VA, Ahluwalia MS. Targeted Therapy in Brain Metastases: Ready for Primetime? Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2016;35:e123–30. doi: 10.14694/EDBK_100006 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(10):947–57. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0810699 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fukuoka M, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Sunpaweravong P, Leong SS, Sriuranpong V, et al. Biomarker analyses and final overall survival results from a phase III, randomized, open-label, first-line study of gefitinib versus carboplatin/paclitaxel in clinically selected patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer in Asia (IPASS). J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(21):2866–74. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.33.4235 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Han JY, Park K, Kim SW, Lee DH, Kim HY, Kim HT, et al. First-SIGNAL: first-line single-agent iressa versus gemcitabine and cisplatin trial in never-smokers with adenocarcinoma of the lung. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(10):1122–8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.36.8456 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Socinski MA, Evans T, Gettinger S, Hensing TA, VanDam Sequist L, Ireland B, et al. Treatment of stage IV non-small cell lung cancer: Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2013;143(5 Suppl):e341S–e68S. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

