FGF 21 deficiency slows gastric emptying and reduces initial blood alcohol concentration in mice exposed to acute alcohol in fasting state
- PMID: 29448103
- PMCID: PMC6044432
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.01.189
FGF 21 deficiency slows gastric emptying and reduces initial blood alcohol concentration in mice exposed to acute alcohol in fasting state
Abstract
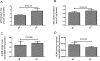
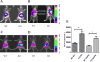
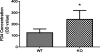
Excess alcohol consumption can lead to alcoholic liver disease. Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is a metabolic regulator with multiple physiologic functions. Previous study demonstrated that FGF21 deficiency exacerbated alcohol-induced liver injury and exogenous FGF21 administration protected liver from chronic alcohol-induced injury. In this study, we aimed to explore the role of FGF21 in alcohol metabolism in mice. FGF21 knockout (KO) mice and the wild type(WT) control mice were divided into two groups and fasted for 24 h followed by a bonus of alcohol treatment at a dose of 5 g/kg body weight via gavage. Serum alcohol concentration was measured after gavage at 0.5, 2, 3, 4 and 6 h, respectively. At the end, gastric and liver tissues were collected. Serum alcohol concentration of KO mice was significantly lower than that of WT at 0.5 h after alcohol expose. There were no significant differences in alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) activity and aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) activity in gastric and liver tissues between WT and the KO mice. However, gastric emptying time of KO mice was much longer than that of WT mice. In addition, the intestinal permeability and serum GLP-1 level of KO mice were significantly higher than that of WT mice. These results suggest that FGF21 deficiency slow gastric emptying rate and indirectly influence initial alcohol metabolism in mice exposed to acute alcohol. Our findings provide additional information for understanding the gastrointestinal mechanism of alcoholic liver disease and other alcohol use disorders.
Keywords: Alcohol; Fibroblast growth factor 21; Gastric emptying.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
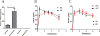
Similar articles
-
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is robustly induced by ethanol and has a protective role in ethanol associated liver injury.Mol Metab. 2017 Nov;6(11):1395-1406. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.08.004. Epub 2017 Aug 19. Mol Metab. 2017. PMID: 29107287 Free PMC article.
-
FGF21 mediates alcohol-induced adipose tissue lipolysis by activation of systemic release of catecholamine in mice.J Lipid Res. 2015 Aug;56(8):1481-91. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M058610. Epub 2015 Jun 19. J Lipid Res. 2015. PMID: 26092866 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor 21 deficiency exacerbates chronic alcohol-induced hepatic steatosis and injury.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 8;6:31026. doi: 10.1038/srep31026. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27498701 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol metabolism in the gastrointestinal tract and its possible consequences.Alcohol Alcohol Suppl. 1994;2:157-62. Alcohol Alcohol Suppl. 1994. PMID: 8974330 Review.
-
Role of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 (FGF21) in the Regulation of Statural Growth.Curr Pediatr Rev. 2015;11(2):98-105. doi: 10.2174/1573396311666150702105152. Curr Pediatr Rev. 2015. PMID: 26133178 Review.
Cited by
-
Enteropathy Markers in Early Life Were Associated with Adipokine, Apolipoprotein, and Cytokine Profiles Consistent with an Adverse Cardiometabolic Disease Risk Profile Later in Childhood in a Peruvian Birth Cohort.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2022 Sep 12;107(4):754-765. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.21-1024. Print 2022 Oct 12. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2022. PMID: 36096405 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol ingestion induces pancreatic islet dysfunction and apoptosis via mediation of FGF21 resistance.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Mar;8(6):310. doi: 10.21037/atm.2020.02.129. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32355754 Free PMC article.
-
The crosstalk between fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) system and substance use.iScience. 2024 Jun 25;27(7):110389. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110389. eCollection 2024 Jul 19. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39055947 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kharitonenkov A. FGFs and metabolism. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009;9:805–810. - PubMed
-
- Fisher FM, Maratos-Flier E. Understanding the Physiology of FGF21. Annu Rev Physiol. 2016;78:223–241. - PubMed
-
- Potthoff MJ. FGF21 and metabolic disease in 2016: A new frontier in FGF21 biology. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13:74–76. - PubMed
-
- Sa-Nguanmoo P, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC. Potential roles of fibroblast growth factor 21 in the brain. Metab Brain Dis. 2016;31:239–248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

