The type 2 diabetes-associated HMG20A gene is mandatory for islet beta cell functional maturity
- PMID: 29449530
- PMCID: PMC5833347
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-018-0272-z
The type 2 diabetes-associated HMG20A gene is mandatory for islet beta cell functional maturity
Abstract
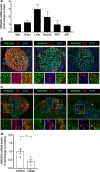
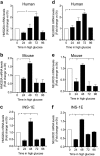
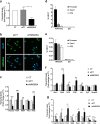
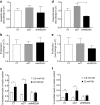
HMG20A (also known as iBRAF) is a chromatin factor involved in neuronal differentiation and maturation. Recently small nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the HMG20A gene have been linked to type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) yet neither expression nor function of this T2DM candidate gene in islets is known. Herein we demonstrate that HMG20A is expressed in both human and mouse islets and that levels are decreased in islets of T2DM donors as compared to islets from non-diabetic donors. In vitro studies in mouse and human islets demonstrated that glucose transiently increased HMG20A transcript levels, a result also observed in islets of gestating mice. In contrast, HMG20A expression was not altered in islets from diet-induced obese and pre-diabetic mice. The T2DM-associated rs7119 SNP, located in the 3' UTR of the HMG20A transcript reduced the luciferase activity of a reporter construct in the human beta 1.1E7 cell line. Depletion of Hmg20a in the rat INS-1E cell line resulted in decreased expression levels of its neuronal target gene NeuroD whereas Rest and Pax4 were increased. Chromatin immunoprecipitation confirmed the interaction of HMG20A with the Pax4 gene promoter. Expression levels of Mafa, Glucokinase, and Insulin were also inhibited. Furthermore, glucose-induced insulin secretion was blunted in HMG20A-depleted islets. In summary, our data demonstrate that HMG20A expression in islet is essential for metabolism-insulin secretion coupling via the coordinated regulation of key islet-enriched genes such as NeuroD and Mafa and that depletion induces expression of genes such as Pax4 and Rest implicated in beta cell de-differentiation. More importantly we assign to the T2DM-linked rs7119 SNP the functional consequence of reducing HMG20A expression likely translating to impaired beta cell mature function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

