Analysis combining correlated glaucoma traits identifies five new risk loci for open-angle glaucoma
- PMID: 29449654
- PMCID: PMC5814451
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-20435-9
Analysis combining correlated glaucoma traits identifies five new risk loci for open-angle glaucoma
Abstract
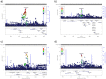
Open-angle glaucoma (OAG) is a major cause of blindness worldwide. To identify new risk loci for OAG, we performed a genome-wide association study in 3,071 OAG cases and 6,750 unscreened controls, and meta-analysed the results with GWAS data for intraocular pressure (IOP) and optic disc parameters (the overall meta-analysis sample size varying between 32,000 to 48,000 participants), which are glaucoma-related traits. We identified and independently validated four novel genome-wide significant associations within or near MYOF and CYP26A1, LINC02052 and CRYGS, LMX1B, and LMO7 using single variant tests, one additional locus (C9) using gene-based tests, and two genetic pathways - "response to fluid shear stress" and "abnormal retina morphology" - in pathway-based tests. Interestingly, some of the new risk loci contribute to risk of other genetically-correlated eye diseases including myopia and age-related macular degeneration. To our knowledge, this study is the first integrative study to combine genetic data from OAG and its correlated traits to identify new risk variants and genetic pathways, highlighting the future potential of combining genetic data from genetically-correlated eye traits for the purpose of gene discovery and mapping.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 EY011671/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004728/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL043851/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA001833/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL073042/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY013178/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY015473/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA047988/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004608/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY013315/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004446/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EY028671/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY018246/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000427/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY011008/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004424/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL073389/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY012118/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY015543/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 EY011671/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006389/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY008208/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA136725/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY019126/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 EY015682/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY022305/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR015574/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA186107/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080467/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA167552/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY009580/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY012118/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY014104/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY015872/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY009847/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA131332/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY010886/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY023512/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY018660/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

