Green tea polyphenols affect invasiveness of human gastric MKN-28 cells by inhibition of LPS or TNF-α induced Matrix Metalloproteinase-9/2
- PMID: 29450132
- PMCID: PMC5802102
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopen.2016.10.002
Green tea polyphenols affect invasiveness of human gastric MKN-28 cells by inhibition of LPS or TNF-α induced Matrix Metalloproteinase-9/2
Abstract
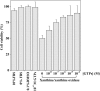
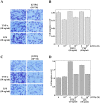
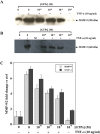
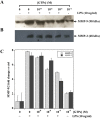
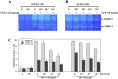
Several studies demonstrated a correlation between green tea consumption and a reduced cancer risk. Among different components, green tea polyphenols have been identified as molecules responsible for the beneficial effects showed by the green tea against oxidative stress and cell invasiveness. In this study, we investigated the effects of green tea polyphenol extracts (GTPs) in human gastric MKN-28 cell line. To this aim, we have first evaluated the effect of GTPs on oxidative stress induced cell injury. The pre-treatment with 10-4 M catechin equivalents of GTPs exerts a protective effect on xanthine-xanthine oxidase induced cell cytotoxicity, thus confirming the anti-oxidant properties of GTPs. The effect of GTPs was also extended to the invasive ability of MKN-28 cells stimulated with TNF-α or LPS, as pro-inflammatory factors. Migration and matrigel invasion assays demonstrated that GTPs exposure (10-6 M) prevents the increase in cell invasiveness induced by TNF-α or LPS. Finally, we have analyzed the effect of GTPs on the levels of Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMP)-9/2, whose expression is up-regulated by TNF-α or LPS. Our results indicated that the pre-treatment with GTPs was able to reduce MMP-9/2 expression at both protein and enzyme activity levels in the conditioned media of TNF-α or LPS stimulated MKN-28 cells. In conclusion, our results demonstrated that green tea polyphenol extract reduces the invasiveness of gastric MKN-28 cancer cells through the reduction of TNF-α or LPS induced MMP-9/2 up-regulation. Therefore, these data support the hypothesis that GTPs could exert a protective role against the metastatic process in gastric cancer.
Keywords: Cell migration; Cell invasion; DMEM, Dulbecco's Modified Eagles's Medium; DMSO, Dimethyl sulfoxide; ECM, Extracellular matrix; FBS, fetal bovine serum; GTPs, Green tea polyphenols extract; Green tea polyphenols; LPS, Lipopolysaccharide; MKN-28 gastric cancer cells; MMP-, Matrix metalloproteinase; Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2); Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9); PBS, Phosphate-buffer saline; ROS, Reactive Oxygen Species; TNF-α, Tumor necrosis factor α.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lemon Peel Polyphenol Extract Reduces Interleukin-6-Induced Cell Migration, Invasiveness, and Matrix Metalloproteinase-9/2 Expression in Human Gastric Adenocarcinoma MKN-28 and AGS Cell Lines.Biomolecules. 2019 Dec 5;9(12):833. doi: 10.3390/biom9120833. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31817563 Free PMC article.
-
Green tea polyphenols prevent lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory liver injury in mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation.Food Funct. 2019 Jul 17;10(7):3898-3908. doi: 10.1039/c9fo00572b. Food Funct. 2019. PMID: 31187838
-
Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase secretion by green tea catechins in a three-dimensional co-culture model of macrophages and gingival fibroblasts.Arch Oral Biol. 2017 Mar;75:89-99. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2016.10.035. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Arch Oral Biol. 2017. PMID: 27825679
-
Antiangiogenic properties of natural polyphenols from red wine and green tea.J Nutr Biochem. 2005 Jan;16(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2004.09.004. J Nutr Biochem. 2005. PMID: 15629234 Review.
-
Dose-dependent functionality and toxicity of green tea polyphenols in experimental rodents.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014 Sep 1;557:3-10. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2014.04.018. Epub 2014 May 9. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014. PMID: 24814373 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Angelica gigas Nakai Ethanol Extract and Decursin on Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells.Molecules. 2020 Apr 27;25(9):2028. doi: 10.3390/molecules25092028. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32349276 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Insight on the Health Benefits and Phytoconstituents of Camellia sinensis and Recent Approaches for Its Quality Control.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Oct 6;8(10):455. doi: 10.3390/antiox8100455. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31590466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Trinity of Matrix Metalloproteinases, Inflammation, and Cancer: A Literature Review of Recent Updates.Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2020;19(3):206-221. doi: 10.2174/1871523018666191023141807. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32178620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lemon Peel Polyphenol Extract Reduces Interleukin-6-Induced Cell Migration, Invasiveness, and Matrix Metalloproteinase-9/2 Expression in Human Gastric Adenocarcinoma MKN-28 and AGS Cell Lines.Biomolecules. 2019 Dec 5;9(12):833. doi: 10.3390/biom9120833. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31817563 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin Inhibits Cell Motility and Proliferation of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells by Blocking HMGB1/RAGE Signaling.Cells. 2025 Apr 13;14(8):590. doi: 10.3390/cells14080590. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40277915 Free PMC article.
References
-
- González C.A., Sala N., Rokkas T. Gastric cancer: epidemiologic aspects. Helicobacter. 2013;18:34–38. - PubMed
-
- Venerito M., Nardone G., Selgrad M., Rokkas T., Malfertheiner P. Gastric cancer-epidemiologic and clinical aspects. Helicobacter. 2014;19:32–37. - PubMed
-
- Fang X., Wei J., He X., An P., Wang H., Jiang L., Shao D., Liang H., Li Y., Wang F., Min J. Landscape of dietary factors associated with risk of gastric cancer: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Eur. J. Cancer. 2015;51:2820–2832. - PubMed
-
- Tallant C., Marrero A., Gomis-Rüth F.X. Matrix metalloproteinases: fold and function of their catalytic domains. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2010;1803:20–28. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

